Page 27 - Parker - The Handbook of Hydraulic Filtration
P. 27
Filter Housing Selection
The Bypass Valve
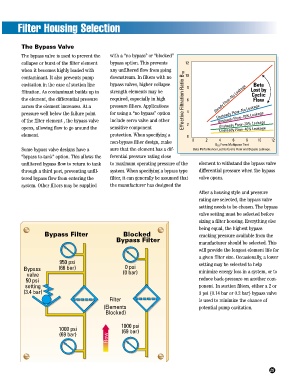
The bypass valve is used to prevent the with a “no bypass” or “blocked”
collapse or burst of the filter element bypass option. This prevents 12
when it becomes highly loaded with any unfiltered flow from going
contaminant. It also prevents pump downstream. In filters with no 10
cavitation in the case of suction line bypass valves, higher collapse 8 Beta
filtration. As contaminant builds up in strength elements may be Lost by
Cyclic
the element, the differential pressure required, especially in high Effective Filtration Ratio B 10 6 Steady Flow–No Leakage Flow
across the element increases. At a pressure filters. Applications
pressure well below the failure point for using a “no bypass” option 4 Unsteady Flow–No Leakage
of the filter element , the bypass valve include servo valve and other Unsteady Flow–10% Leakage
opens, allowing flow to go around the sensitive component 2 Unsteady Flow–20% Leakage
Unsteady Flow–40% Leakage
element. protection. When specifying a 0
non-bypass filter design, make 0 2 4 6 8 10 12
B 10 From Multipass Test
Some bypass valve designs have a sure that the element has a dif- Beta Performance Lost by Cyclic Flow and Bypass Leakage.
“bypass to-tank” option. This allows the ferential pressure rating close
unfiltered bypass flow to return to tank to maximum operating pressure of the element to withstand the bypass valve
through a third port, preventing unfil- system. When specifying a bypass type differential pressure when the bypass
tered bypass flow from entering the filter, it can generally be assumed that valve opens.
system. Other filters may be supplied the manufacturer has designed the
After a housing style and pressure
rating are selected, the bypass valve
setting needs to be chosen. The bypass
valve setting must be selected before
sizing a filter housing. Everything else
being equal, the highest bypass
Bypass Filter Blocked cracking pressure available from the
Bypass Filter
manufacturer should be selected. This
will provide the longest element life for
a given filter size. Occasionally, a lower
950 psi setting may be selected to help
Bypass (66 bar) 0 psi minimize energy loss in a system, or to
valve (0 bar)
50 psi reduce back-pressure on another com-
setting ponent. In suction filters, either a 2 or
(3.4 bar) 3 psi (0.14 bar or 0.2 bar) bypass valve
Filter is used to minimize the chance of
(Elements potential pump cavitation.
Blocked)
1000 psi
1000 psi (69 bar)
(69 bar)
Flow
25