Page 60 - Human anatomy COMPLETELY DONE1
P. 60
the reduction of the annular and radial muscle fibers of the iris.
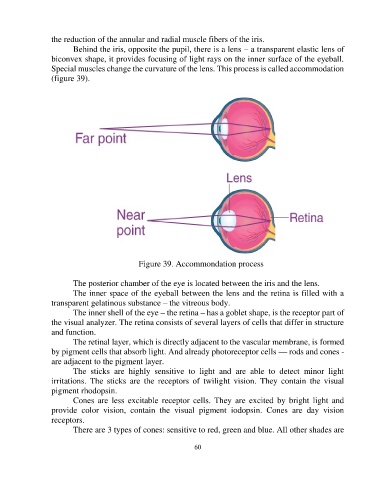
Behind the iris, opposite the pupil, there is a lens – a transparent elastic lens of
biconvex shape, it provides focusing of light rays on the inner surface of the eyeball.
Special muscles change the curvature of the lens. This process is called accommodation
(figure 39).
Figure 39. Accommondation process
The posterior chamber of the eye is located between the iris and the lens.
The inner space of the eyeball between the lens and the retina is filled with a
transparent gelatinous substance – the vitreous body.
The inner shell of the eye – the retina – has a goblet shape, is the receptor part of
the visual analyzer. The retina consists of several layers of cells that differ in structure
and function.
The retinal layer, which is directly adjacent to the vascular membrane, is formed
by pigment cells that absorb light. And already photoreceptor cells — rods and cones -
are adjacent to the pigment layer.
The sticks are highly sensitive to light and are able to detect minor light
irritations. The sticks are the receptors of twilight vision. They contain the visual
pigment rhodopsin.
Cones are less excitable receptor cells. They are excited by bright light and
provide color vision, contain the visual pigment iodopsin. Cones are day vision
receptors.
There are 3 types of cones: sensitive to red, green and blue. All other shades are
60