Page 189 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 189
MECHANISMS FOR MOTION TRANSMISSION 175
Gear shift
lever
R to synchronizers S1, S2, S3
G4
G3
G2 G1
Gear
1 Gear Gear
Clutch 2 3 Gear Gear Output
4 reverse shaft to
N eng S1 differential
w out
w in
From
engine S2 N 62 S3
N 12 N 22
Idles to
reverse
direction
N 61
N 11
N 21
N 0 Counter shaft
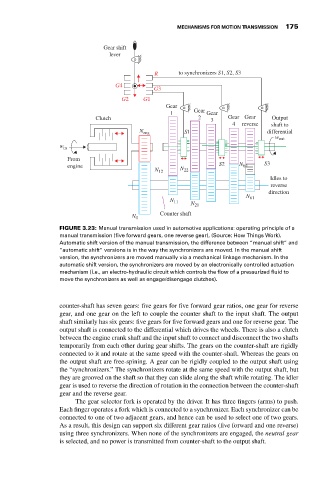
FIGURE 3.23: Manual transmission used in automotive applications: operating principle of a
manual transmission (five forward gears, one reverse gear), (Source: How Things Work).
Automatic shift version of the manual transmission, the difference between “manual shift” and
“automatic shift” versions is in the way the synchronizers are moved. In the manual shift
version, the synchronizers are moved manually via a mechanical linkage mechanism. In the
automatic shift version, the synchronizers are moved by an electronically controlled actuation
mechanism (i.e., an electro-hydraulic circuit which controls the flow of a pressurized fluid to
move the synchronizers as well as engage/disengage clutches).
counter-shaft has seven gears: five gears for five forward gear ratios, one gear for reverse
gear, and one gear on the left to couple the counter shaft to the input shaft. The output
shaft similarly has six gears: five gears for five forward gears and one for reverse gear. The
output shaft is connected to the differential which drives the wheels. There is also a clutch
between the engine crank shaft and the input shaft to connect and disconnect the two shafts
temporarily from each other during gear shifts. The gears on the counter-shaft are rigidly
connected to it and rotate at the same speed with the counter-shaft. Whereas the gears on
the output shaft are free-spining. A gear can be rigidly coupled to the output shaft using
the “synchronizers.” The synchronizers rotate at the same speed with the output shaft, but
they are grooved on the shaft so that they can slide along the shaft while rotating. The idler
gear is used to reverse the direction of rotation in the connection between the counter-shaft
gear and the reverse gear.
The gear selector fork is operated by the driver. It has three fingers (arms) to push.
Each finger operates a fork which is connected to a synchronizer. Each synchronizer can be
connected to one of two adjacent gears, and hence can be used to select one of two gears.
As a result, this design can support six different gear ratios (five forward and one reverse)
using three synchronizers. When none of the synchronizers are engaged, the neutral gear
is selected, and no power is transmitted from counter-shaft to the output shaft.