Page 212 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 212
198 MECHATRONICS
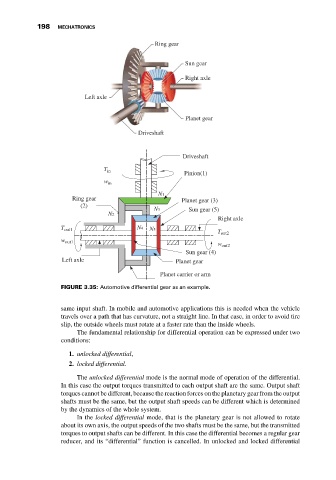
Ring gear
Sun gear
Right axle
Left axle
Planet gear
Driveshaft
Driveshaft
T in
Pinion(1)
w in
N1
Ring gear Planet gear (3)
(2)
N3 Sun gear (5)
N2
Right axle
T out1 N4 N5
T out2
w out1
w out2
Sun gear (4)
Left axle Planet gear
Planet carrier or arm
FIGURE 3.35: Automotive differential gear as an example.
same input shaft. In mobile and automotive applications this is needed when the vehicle
travels over a path that has curvature, not a straight line. In that case, in order to avoid tire
slip, the outside wheels must rotate at a faster rate than the inside wheels.
The fundamental relationship for differential operation can be expressed under two
conditions:
1. unlocked differential,
2. locked differential.
The unlocked differential mode is the normal mode of operation of the differential.
In this case the output torques transmitted to each output shaft are the same. Output shaft
torques cannot be different, because the reaction forces on the planetary gear from the output
shafts must be the same, but the output shaft speeds can be different which is determined
by the dynamics of the whole system.
In the locked differential mode, that is the planetary gear is not allowed to rotate
about its own axis, the output speeds of the two shafts must be the same, but the transmitted
torques to output shafts can be different. In this case the differential becomes a regular gear
reducer, and its “differential” function is cancelled. In unlocked and locked differential