Page 356 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 356
JWST499-Cetinkunt
JWST499-c06
342 MECHATRONICS Printer: Yet to Come October 9, 2014 8:1 254mm×178mm
steel rod is used to connect the core to the part whose displacement is to be measured. The
sign (direction) of the magnitude of the voltage differential is determined by relating the
induced voltage phase to the reference voltage phase. It is a function of the direction of
the magnetic core displacement from neutral position. The primary winding is excited by
V (t) = V ⋅ sin(w t) (6.49)
r
r
p
and the voltage differential between the secondary windings is
V (t) = k ⋅ V (t) ⋅ x(t) (6.50)
0
p
s
= k ⋅ V ⋅ sin(w t) ⋅ x(t) (6.51)
0
r
r
Once the the V (t) is demodulated in frequency, the output signal is presented as a DC
s
voltage,
V out (t) = k ⋅ x(t) (6.52)
1
which is proportional to the core displacement.
LVDTs can be used for high resolution position measurement (i.e., 1∕10 000 in res-
olution) but with a relatively small range (up to 10 in range). Excitation frequency of the
primary coil is in the range of 50 Hz to 25 kHz. The bandwidth of the sensor is about 1∕10
of the excitation frequency (Figure 6.12).
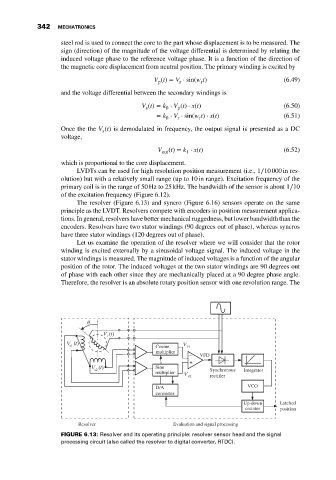
The resolver (Figure 6.13) and syncro (Figure 6.16) sensors operate on the same
principle as the LVDT. Resolvers compete with encoders in position measurement applica-
tions. In general, resolvers have better mechanical ruggedness, but lower bandwidth than the
encoders. Resolvers have two stator windings (90 degrees out of phase), whereas syncros
have three stator windings (120 degrees out of phase).
Let us examine the operation of the resolver where we will consider that the rotor
winding is excited externally by a sinusoidal voltage signal. The induced voltage in the
stator windings is measured. The magnitude of induced voltages is a function of the angular
position of the rotor. The induced voltages at the two stator windings are 90 degrees out
of phase with each other since they are mechanically placed at a 90 degree phase angle.
Therefore, the resolver is an absolute rotary position sensor with one revolution range. The
Cosine
multiplier
VFD
Sine Synchronous
multiplier Integrator
rectifier
D/A VCO
converter
Up-down Latched
counter position
Resolver Evaluation and signal processing
FIGURE 6.13: Resolver and its operating principle: resolver sensor head and the signal
processing circuit (also called the resolver to digital converter, RTDC).