Page 61 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 61
CLOSED LOOP CONTROL 47
u(t)
u(KT)
Clock y(t)
D/A
Actuators Process
DO
CPU
x = f(x,u) DI
u =.......
Sensors
A/D
Picture of an embedded y(KT)
controller Digital controller
y(t) y(kT) u(kT) u(t)
t 0T2T............ t 0T2T............ t t
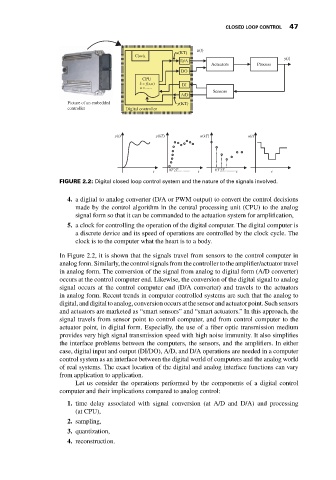
FIGURE 2.2: Digital closed loop control system and the nature of the signals involved.
4. a digital to analog converter (D/A or PWM output) to convert the control decisions
made by the control algorithm in the central processing unit (CPU) to the analog
signal form so that it can be commanded to the actuation system for amplification,
5. a clock for controlling the operation of the digital computer. The digital computer is
a discrete device and its speed of operations are controlled by the clock cycle. The
clock is to the computer what the heart is to a body.
In Figure 2.2, it is shown that the signals travel from sensors to the control computer in
analog form. Similarly, the control signals from the controller to the amplifier/actuator travel
in analog form. The conversion of the signal from analog to digital form (A/D converter)
occurs at the control computer end. Likewise, the conversion of the digital signal to analog
signal occurs at the control computer end (D/A converter) and travels to the actuators
in analog form. Recent trends in computer controlled systems are such that the analog to
digital, and digital to analog, conversion occurs at the sensor and actuator point. Such sensors
and actuators are marketed as “smart sensors” and “smart actuators.” In this approach, the
signal travels from sensor point to control computer, and from control computer to the
actuator point, in digital form. Especially, the use of a fiber optic transmission medium
provides very high signal transmission speed with high noise immunity. It also simplifies
the interface problems between the computers, the sensors, and the amplifiers. In either
case, digital input and output (DI/DO), A/D, and D/A operations are needed in a computer
control system as an interface between the digital world of computers and the analog world
of real systems. The exact location of the digital and analog interface functions can vary
from application to application.
Let us consider the operations performed by the components of a digital control
computer and their implications compared to analog control:
1. time delay associated with signal conversion (at A/D and D/A) and processing
(at CPU),
2. sampling,
3. quantization,
4. reconstruction.