Page 80 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 80
66 MECHATRONICS
variations in process dynamics. This is the fundamental design conflict of feedback control
systems. Robustness against disturbances and variations in process dynamics require large
loop gain balanced between controller and process, D(s)G(s) ≫ 1, while robustness against
sensor noise requires D(s)G(s) ≪ 1. These are conflicting requirements and both cannot be
satisfied at the same time for all frequencies.
In practice, the control engineering problems are generally such that disturbances and
variations in process dynamics are slowly varying and have low frequency content. Whereas
sensor noise has high frequency content. If a given control problem has this frequency
separation property between various uncertainties, then a controller can be designed such
that D(s)G(s) ≫ 1, D(s), G(s) for a low frequency range so that the system has good
robustness against disturbances and variations in process dynamics, and D(s)G(s) ≪ 1for
a high frequency range so that sensor noise is also rejected. This is the basic feedback control
system design compromise. If there is no such frequency separation between disturbance,
variations in process dynamics, and sensor noise, no feedback controller can be designed
to provide robustness against all of these real-world problems.
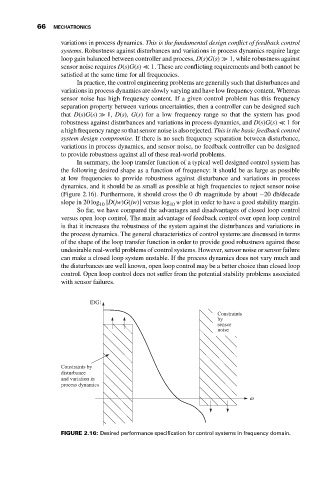
In summary, the loop transfer function of a typical well designed control system has
the following desired shape as a function of frequency: it should be as large as possible
at low frequencies to provide robustness against disturbance and variations in process
dynamics, and it should be as small as possible at high frequencies to reject sensor noise
(Figure 2.16). Furthermore, it should cross the 0 db magnitude by about −20 db/decade
slope in 20 log |D(jw)G(jw)| versus log w plot in order to have a good stability margin.
10 10
So far, we have compared the advantages and disadvantages of closed loop control
versus open loop control. The main advantage of feedback control over open loop control
is that it increases the robustness of the system against the disturbances and variations in
the process dynamics. The general characteristics of control systems are discussed in terms
of the shape of the loop transfer function in order to provide good robustness against these
undesirable real-world problems of control systems. However, sensor noise or sensor failure
can make a closed loop system unstable. If the process dynamics does not vary much and
the disturbances are well known, open loop control may be a better choice than closed loop
control. Open loop control does not suffer from the potential stability problems associated
with sensor failures.
|DG|
Constraints
by
sensor
noise
Constraints by
disturbance
and variation in
process dynamics
ω
FIGURE 2.16: Desired performance specification for control systems in frequency domain.