Page 116 - Pharmaceutical Organic Chemmistry-3 (Theoritical book) 24-25
P. 116
Clinical Pharmacy PharmD - 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-3 (PC 305)
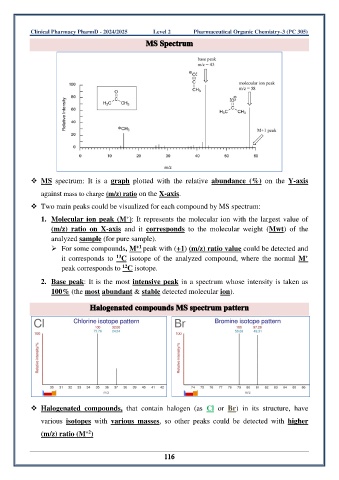
❖ MS spectrum: It is a graph plotted with the relative abundance (%) on the Y-axis
against mass to charge (m/z) ratio on the X-axis.
❖ Two main peaks could be visualized for each compound by MS spectrum:
+
1. Molecular ion peak (M ): It represents the molecular ion with the largest value of
(m/z) ratio on X-axis and it corresponds to the molecular weight (Mwt) of the
analyzed sample (for pure sample).
+1
➢ For some compounds, M peak with (+1) (m/z) ratio value could be detected and
+
13
it corresponds to C isotope of the analyzed compound, where the normal M
12
peak corresponds to C isotope.
2. Base peak: It is the most intensive peak in a spectrum whose intensity is taken as
100% (the most abundant & stable detected molecular ion).
❖ Halogenated compounds, that contain halogen (as Cl or Br) in its structure, have
various isotopes with various masses, so other peaks could be detected with higher
+2
(m/z) ratio (M )