Page 40 - Pharmaceutical Organic Chemmistry-3 (Theoritical book) 24-25
P. 40
Clinical Pharmacy PharmD - 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-3 (PC 305)
2- Furan and its derivatives
Furan is the oxygen analogue of the 5-membered heterocyclic aromatic compounds.
General methods of preparation:
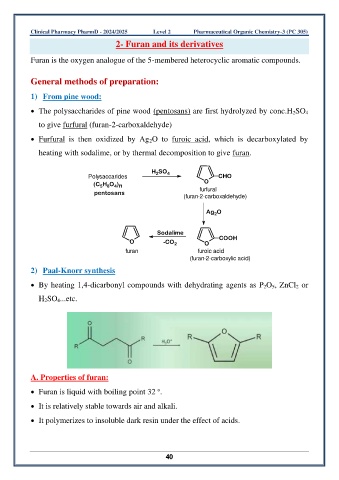
1) From pine wood:
• The polysaccharides of pine wood (pentosans) are first hydrolyzed by conc.H 2SO 4
to give furfural (furan-2-carboxaldehyde)
• Furfural is then oxidized by Ag 2O to furoic acid, which is decarboxylated by
heating with sodalime, or by thermal decomposition to give furan.
H SO
Polysaccarides 2 4 CHO
(C H O ) O
4 n
5 8
pentosans furfural
(furan-2-carboxaldehyde)
Ag O
2
Sodalime
O -CO 2 O COOH
furan furoic acid
(furan-2-carboxylic acid)
2) Paal-Knorr synthesis
• By heating 1,4-dicarbonyl compounds with dehydrating agents as P 2O 5, ZnCl 2 or
H 2SO 4...etc.
A. Properties of furan:
o
• Furan is liquid with boiling point 32 .
• It is relatively stable towards air and alkali.
• It polymerizes to insoluble dark resin under the effect of acids.