Page 142 - M97TB9_2018-19_[low-res]_F2F_Neat2
P. 142
6/10 M97/February 2018 Reinsurance
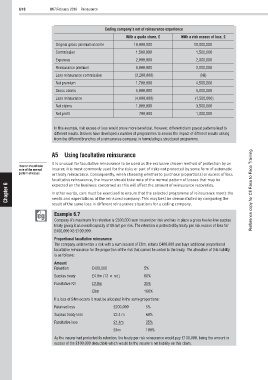
Ceding company’s net of reinsurance experience
With a quota share, £ With a risk excess of loss, £
Original gross premium income 10,000,000 10,000,000
Commission 1,500,000 1,500,000
Expenses 2,000,000 2,000,000
Reinsurance premium 8,000,000 2,000,000
Less reinsurance commission (3,200,000) (Nil)
Net premium 1,700,000 4,500,000
Gross claims 5,000,000 5,000,000
Less reinsurance (4,000,000) (1,500,000)
Net claims 1,000,000 3,500,000
Net profit 700,000 1,000,000
In this example, risk excess of loss would prove more beneficial. However, different claim payout patterns lead to
different results. Brokers have developed a number of programmes to assess the impact of different results arising
from the different branches of a reinsurance company, in formulating a structured programme.
A5 Using facultative reinsurance
It is unusual for facultative reinsurance to be used as the exclusive chosen method of protection by an
Insurer should take
note of the normal insurer; it is most commonly used for the risks or part of risks not protected by some form of automatic
pattern of losses or treaty reinsurance. Consequently, when choosing whether to purchase proportional or excess of loss
facultative reinsurance, the insurer should take note of the normal pattern of losses that may be
6 expected on the business concerned as this will affect the amount of reinsurance recoveries.
Chapter In other words, care must be exercised to ensure that the selected programme of reinsurance meets the Reference copy for CII Face to Face Training
needs and expectations of the reinsured company. This may best be demonstrated by comparing the
result of the same loss in different reinsurance situations for a ceding company.
Example 6.7
Company A’s maximum fire retention is £500,000 sum insured per risk and has in place a gross twelve-line surplus
treaty giving it an overall capacity of £6.5m per risk. The retention is protected by treaty per risk excess of loss for
£400,000 XS £100,000.
Proportional facultative reinsurance
The company underwrites a risk with a sum insured of £8m, retains £400,000 and buys additional proportional
facultative reinsurance for the proportion of the risk that cannot be ceded to the treaty. The allocation of this liability
is as follows:
Amount
Retention £400,000 5%
Surplus treaty £4.8m (12 × ret.) 60%
Facultative R/I £2.8m 35%
£8m 100%
If a loss of £4m occurs it must be allocated in the same proportions:
Retained loss £200,000 5%
Surplus treaty loss £2.4 m 60%
Facultative loss £1.4m 35%
£4m 100%
As the insurer had protected its retention, the treaty per risk reinsurance would pay £100,000, being the amount in
excess of the £100,000 deductible which would be the insurer’s net liability on this claim.