Page 216 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 216
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
2- Cholecystitis:
▪ Cholecystitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the gall bladder.
▪ It is most commonly caused by the presence of gallstones in the gall bladder,
▪ but may also result from infection or reduced blood flow to the gall bladder.
▪ Signs and symptoms are similar to those observed with cholelithiasis.
❖ Liver Disorders
1- Viral hepatitis
▪ The term hepatitis refers to inflammation and possible injury of the liver.
▪ Hepatitis may be caused by a number of injurious agents such as viruses, alcohol, toxins and drugs.
▪ When the liver is inflamed and injured as a result of viral infection it is termed a Viral Hepatitis.
▪ The main hepatitis viruses are A, B, C, D and E.
▪ All of the hepatitis viruses target the hepatocytes of the liver as their site of infection and
replication.
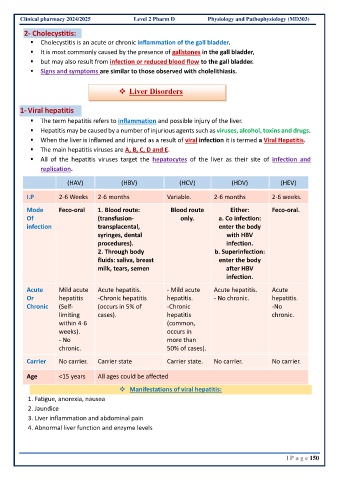
(HAV) (HBV) (HCV) (HDV) (HEV)
I.P 2-6 Weeks 2-6 months Variable. 2-6 months 2-6 weeks.
Mode Feco-oral 1. Blood route: Blood route Either: Feco-oral.
Of (transfusion- only. a. Co infection:
infection transplacental, enter the body
syringes, dental with HBV
procedures). infection.
2. Through body b. Superinfection:
fluids: saliva, breast enter the body
milk, tears, semen after HBV
infection.
Acute Mild acute Acute hepatitis. - Mild acute Acute hepatitis. Acute
Or hepatitis -Chronic hepatitis hepatitis. - No chronic. hepatitis.
Chronic (Self- (occurs in 5% of -Chronic -No
limiting cases). hepatitis chronic.
within 4-6 (common,
weeks). occurs in
- No more than
chronic. 50% of cases).
Carrier No carrier. Carrier state Carrier state. No carrier. No carrier.
Age <15 years All ages could be affected
❖ Manifestations of viral hepatitis:
1. Fatigue, anorexia, nausea
2. Jaundice
3. Liver inflammation and abdominal pain
4. Abnormal liver function and enzyme levels
| P a g e 150