Page 217 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 217
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
▪ Jaundice:
o Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes due to excess levels of circulating bilirubin.
o Bilirubin is the pigment portion of bile. Bilirubin is formed from hemoglobin during the normal
and abnormal breakdown of RBCs.
o Free bilirubin formed in the blood is conjugated by the liver and eliminated into the intestinal
tract along with bile.
o Any condition that impairs the ability of the liver to conjugate and eliminate bilirubin will result in
the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood with the occurrence of jaundice.
❖ Possible complications of hepatitis:
1. Chronic active or persistent hepatitis can lead to progressive liver injury, liver failure and death.
2. Chronic active hepatitis is also associated with an increased incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma.
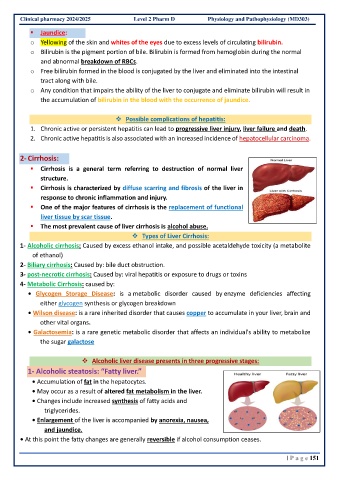
2- Cirrhosis:
▪ Cirrhosis is a general term referring to destruction of normal liver
structure.
▪ Cirrhosis is characterized by diffuse scarring and fibrosis of the liver in
response to chronic inflammation and injury.
▪ One of the major features of cirrhosis is the replacement of functional
liver tissue by scar tissue.
▪ The most prevalent cause of liver cirrhosis is alcohol abuse.
❖ Types of Liver Cirrhosis:
1- Alcoholic cirrhosis: Caused by excess ethanol intake, and possible acetaldehyde toxicity (a metabolite
of ethanol)
2- Biliary cirrhosis: Caused by: bile duct obstruction.
3- post-necrotic cirrhosis: Caused by: viral hepatitis or exposure to drugs or toxins
4- Metabolic Cirrhosis: caused by:
• Glycogen Storage Disease: is a metabolic disorder caused by enzyme deficiencies affecting
either glycogen synthesis or glycogen breakdown
• Wilson disease: is a rare inherited disorder that causes copper to accumulate in your liver, brain and
other vital organs.
• Galactosemia: is a rare genetic metabolic disorder that affects an individual's ability to metabolize
the sugar galactose
❖ Alcoholic liver disease presents in three progressive stages:
1- Alcoholic steatosis: “Fatty liver.”
• Accumulation of fat in the hepatocytes.
• May occur as a result of altered fat metabolism in the liver.
• Changes include increased synthesis of fatty acids and
triglycerides.
• Enlargement of the liver is accompanied by anorexia, nausea,
and jaundice.
• At this point the fatty changes are generally reversible if alcohol consumption ceases.
| P a g e 151