Page 213 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 213
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
❖ Manifestations:
1- Burning pain in the epigastric region (“heartburn”) that may be worsened by alcohol consumption,
caffeine, smoking, exercise, obesity and by lying down.
2- Esophagitis, possible ulceration of esophagus.
3- Dysphagia, poor nutrition.
4- Possible increased risk of esophageal cancer.
❖ Stomach Disorders
1- Gastritis
▪ Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric
mucosa (stomach lining).
▪ It may present as an acute or chronic disorder.
Acute Gastritis Chronic Gastritis
Transient irritation and inflammation of the Chronic irritation and inflammation of the
stomach lining. stomach lining.
May be caused by: May be caused by:
- Alcohol consumption - Bacterial infection
- Aspirin use - Alcohol abuse
- Stress. - Long-term aspirin and (NSAID) use.
The inflammation associated with acute Can lead to:
gastritis is a self-limiting process that does atrophy
not usually result in long-term injury to the ulceration of the gastric mucosa.
gastric mucosa.
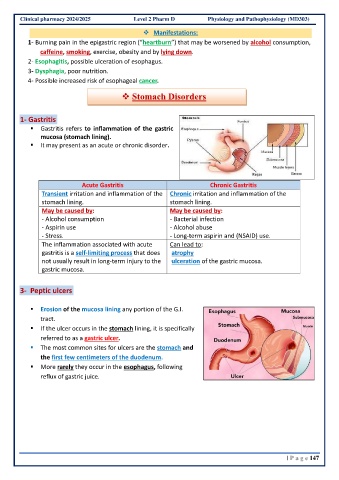
3- Peptic ulcers
▪ Erosion of the mucosa lining any portion of the G.I.
tract.
▪ If the ulcer occurs in the stomach lining, it is specifically
referred to as a gastric ulcer.
▪ The most common sites for ulcers are the stomach and
the first few centimeters of the duodenum.
▪ More rarely they occur in the esophagus, following
reflux of gastric juice.
| P a g e 147