Page 223 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 223
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
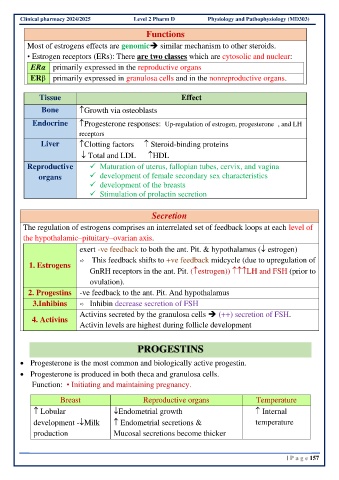
Functions
Most of estrogens effects are genomic➔ similar mechanism to other steroids.
• Estrogen receptors (ERs): There are two classes which are cytosolic and nuclear:
ERα primarily expressed in the reproductive organs
ERβ primarily expressed in granulosa cells and in the nonreproductive organs.
Tissue Effect
Bone Growth via osteoblasts
Endocrine Progesterone responses: Up-regulation of estrogen, progesterone , and LH
receptors
Liver Clotting factors Steroid-binding proteins
Total and LDL HDL
Reproductive ✓ Maturation of uterus, fallopian tubes, cervix, and vagina
organs ✓ development of female secondary sex characteristics
✓ development of the breasts
✓ Stimulation of prolactin secretion
Secretion
The regulation of estrogens comprises an interrelated set of feedback loops at each level of
the hypothalamic–pituitary–ovarian axis.
exert -ve feedback to both the ant. Pit. & hypothalamus ( estrogen)
This feedback shifts to +ve feedback midcycle (due to upregulation of
1. Estrogens
GnRH receptors in the ant. Pit. (estrogen)) LH and FSH (prior to
ovulation).
2. Progestins -ve feedback to the ant. Pit. And hypothalamus
3.Inhibins Inhibin decrease secretion of FSH
Activins secreted by the granulosa cells ➔ (++) secretion of FSH.
4. Activins
Activin levels are highest during follicle development
PROGESTINS
• Progesterone is the most common and biologically active progestin.
• Progesterone is produced in both theca and granulosa cells.
Function: • Initiating and maintaining pregnancy.
Breast Reproductive organs Temperature
Lobular Endometrial growth Internal
development -Milk Endometrial secretions & temperature
production Mucosal secretions become thicker
| P a g e 157