Page 227 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 227
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
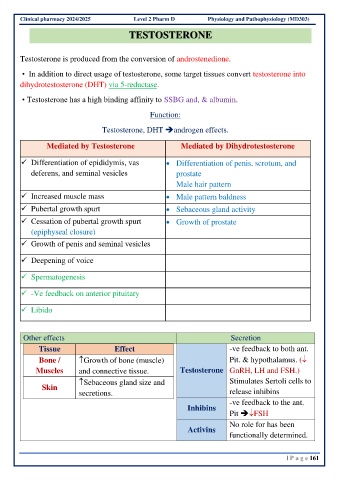
TESTOSTERONE
Testosterone is produced from the conversion of androstenedione.
• In addition to direct usage of testosterone, some target tissues convert testosterone into
dihydrotestosterone (DHT) via 5-reductase.
• Testosterone has a high binding affinity to SSBG and, & albumin.
Function:
Testosterone, DHT ➔androgen effects.
Mediated by Testosterone Mediated by Dihydrotestosterone
✓ Differentiation of epididymis, vas • Differentiation of penis, scrotum, and
deferens, and seminal vesicles prostate
Male hair pattern
✓ Increased muscle mass • Male pattern baldness
✓ Pubertal growth spurt • Sebaceous gland activity
✓ Cessation of pubertal growth spurt • Growth of prostate
(epiphyseal closure)
✓ Growth of penis and seminal vesicles
✓ Deepening of voice
✓ Spermatogenesis
✓ -Ve feedback on anterior pituitary
✓ Libido
Other effects Secretion
Tissue Effect -ve feedback to both ant.
Bone / Growth of bone (muscle) Pit. & hypothalamus. (
Muscles and connective tissue. Testosterone GnRH, LH and FSH.)
Sebaceous gland size and Stimulates Sertoli cells to
Skin
secretions. release inhibins
-ve feedback to the ant.
Inhibins
Pit ➔FSH
No role for has been
Activins
functionally determined.
| P a g e 161