Page 31 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 31
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
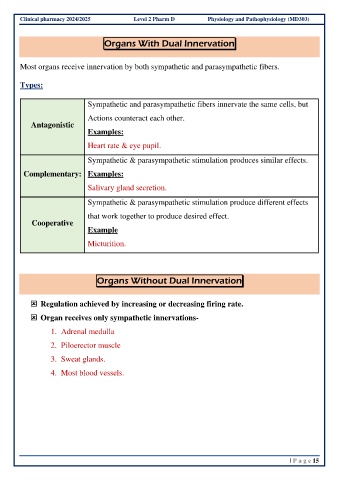
Organs With Dual Innervation
Most organs receive innervation by both sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers.
Types:
Sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers innervate the same cells, but
Actions counteract each other.
Antagonistic
Examples:
Heart rate & eye pupil.
Sympathetic & parasympathetic stimulation produces similar effects.
Complementary: Examples:
Salivary gland secretion.
Sympathetic & parasympathetic stimulation produce different effects
that work together to produce desired effect.
Cooperative
Example
Micturition.
Organs Without Dual Innervation
Regulation achieved by increasing or decreasing firing rate.
Organ receives only sympathetic innervations-
1. Adrenal medulla
2. Piloerector muscle
3. Sweat glands.
4. Most blood vessels.
| P a g e 15