Page 51 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 51
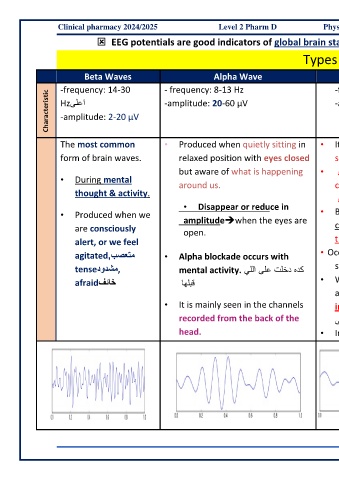
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
EEG potentials are good indicators of global brain statedisplay rhythmic patterns at characteristic frequencies.
Types of waves
-frequency: 14-30 - frequency: 8-13 Hz -frequency: 4-7Hz -frequency:0.5-3.5 Hz -frequency: 36-44Hz
Beta Waves
Delta Waves
Gamma Waves
Alpha Wave
Theta Waves:
Characteristic Hz ىلعا -amplitude: 20-60 µV -amplitude: 20-100µV -amplitude: 20-200µV -amplitude: 3-5µV
-amplitude: 2-20 µV
The most common • Produced when quietly sitting in • It is a state of • Found during periods • Occur with
form of brain waves. relaxed position with eyes closed somnolence. of deep sleep(non- sudden sensory
but aware of what is happening • سوعنمwith reduced dreamy) or stimuli.
• During mental
ن
around us. consciousness. كمم unconsciousness
thought & activity. • More frequency
قوفي (Coma) in most people.
• Disappear or reduce in than Beta
• Produced when we • Believed to be more
amplitude➔when the eyes are • Characterized by very
are consciously common in children
open. irregular and slow
alert, or we feel than adults. wave patterns
agitated,بصعتم • Alpha blockade occurs with • Occur in emotional
tenseدودشم, mental activity. يللا ىلع تلخد هدك stress.
afraidفئاخ اهلبق • Waves with
amplitudes of 100µV
• It is mainly seen in the channels in babies feeding ام لوا
recorded from the back of the ىحصي اهليشت
head. • In REM sleep (dream)
| P a g e 32