Page 104 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 104
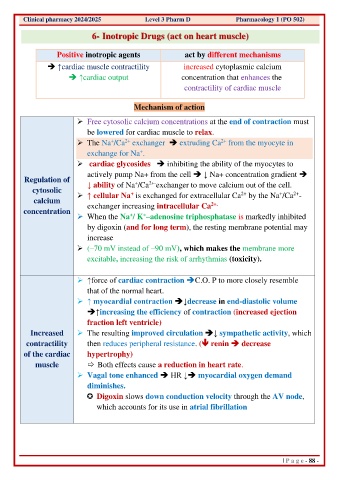
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
6- Inotropic Drugs (act on heart muscle)
Positive inotropic agents act by different mechanisms
➔ ↑cardiac muscle contractility increased cytoplasmic calcium
➔ ↑cardiac output concentration that enhances the
contractility of cardiac muscle
Mechanism of action
➢ Free cytosolic calcium concentrations at the end of contraction must
be lowered for cardiac muscle to relax.
+
2+
➢ The Na /Ca exchanger ➔ extruding Ca from the myocyte in
2+
+
exchange for Na .
➢ cardiac glycosides ➔ inhibiting the ability of the myocytes to
actively pump Na+ from the cell ➔ ↓ Na+ concentration gradient ➔
Regulation of ↓ ability of Na /Ca exchanger to move calcium out of the cell.
+
2+-
cytosolic ➢ ↑ cellular Na is exchanged for extracellular Ca by the Na /Ca -
2+
+
2+
+
calcium exchanger increasing intracellular Ca
2+.
concentration
+
+
➢ When the Na / K –adenosine triphosphatase is markedly inhibited
by digoxin (and for long term), the resting membrane potential may
increase
➢ (–70 mV instead of –90 mV), which makes the membrane more
excitable, increasing the risk of arrhythmias (toxicity).
➢ ↑force of cardiac contraction ➔C.O. P to more closely resemble
that of the normal heart.
➢ ↑ myocardial contraction ➔↓decrease in end-diastolic volume
➔↑increasing the efficiency of contraction (increased ejection
fraction left ventricle)
Increased ➢ The resulting improved circulation ➔↓ sympathetic activity, which
contractility then reduces peripheral resistance. ( renin ➔ decrease
of the cardiac hypertrophy)
muscle Both effects cause a reduction in heart rate.
➢ Vagal tone enhanced ➔ HR ↓➔ myocardial oxygen demand
diminishes.
Digoxin slows down conduction velocity through the AV node,
which accounts for its use in atrial fibrillation
| P a g e - 88 -