Page 106 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 106
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
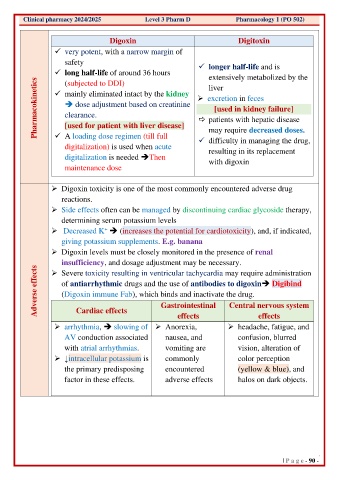
Digoxin Digitoxin
✓ very potent, with a narrow margin of
safety ✓ longer half-life and is
✓ long half-life of around 36 hours extensively metabolized by the
Pharmacokinetics ✓ mainly eliminated intact by the kidney ➢ excretion in feces
(subjected to DDI)
liver
➔ dose adjustment based on creatinine
[used in kidney failure]
clearance.
patients with hepatic disease
[used for patient with liver disease]
may require decreased doses.
✓ A loading dose regimen (till full
digitalization) is used when acute ✓ difficulty in managing the drug,
resulting in its replacement
digitalization is needed ➔Then with digoxin
maintenance dose
➢ Digoxin toxicity is one of the most commonly encountered adverse drug
reactions.
➢ Side effects often can be managed by discontinuing cardiac glycoside therapy,
determining serum potassium levels
+
➢ Decreased K ➔ (increases the potential for cardiotoxicity), and, if indicated,
giving potassium supplements. E.g. banana
➢ Digoxin levels must be closely monitored in the presence of renal
insufficiency, and dosage adjustment may be necessary.
Adverse effects of antiarrhythmic drugs and the use of antibodies to digoxin➔ Digibind
➢ Severe toxicity resulting in ventricular tachycardia may require administration
(Digoxin immune Fab), which binds and inactivate the drug.
Central nervous system
Gastrointestinal
Cardiac effects
effects
effects
➢ arrhythmia, ➔ slowing of ➢ Anorexia, ➢ headache, fatigue, and
AV conduction associated nausea, and confusion, blurred
with atrial arrhythmias. vomiting are vision, alteration of
➢ ↓intracellular potassium is commonly color perception
the primary predisposing encountered (yellow & blue), and
factor in these effects. adverse effects halos on dark objects.
| P a g e - 90 -