Page 121 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 121
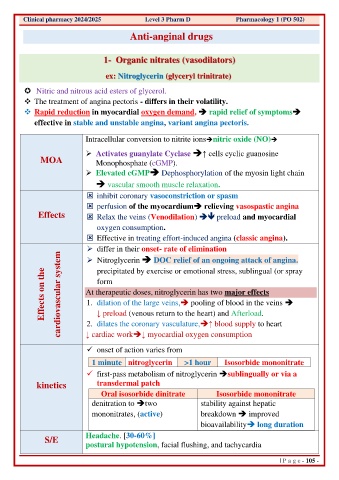
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
Anti-anginal drugs
1- Organic nitrates (vasodilators)
ex: Nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate
(
Nitric and nitrous acid esters of glycerol.
❖ The treatment of angina pectoris - differs in their volatility.
❖ Rapid reduction in myocardial oxygen demand, ➔ rapid relief of symptoms➔
effective in stable and unstable angina, variant angina pectoris.
Intracellular conversion to nitrite ions➔nitric oxide (NO)➔
➢ Activates guanylate Cyclase ➔↑ cells cyclic guanosine
MOA Monophosphate (cGMP).
➢ Elevated cGMP➔ Dephosphorylation of the myosin light chain
➔ vascular smooth muscle relaxation.
inhibit coronary vasoconstriction or spasm
perfusion of the myocardium➔ relieving vasospastic angina
Effects Relax the veins (Venodilation) ➔ preload and myocardial
oxygen consumption.
Effective in treating effort-induced angina (classic angina).
➢ differ in their onset- rate of elimination
➢ Nitroglycerin ➔ DOC relief of an ongoing attack of angina.
Effects on the cardiovascular system At therapeutic doses, nitroglycerin has two major effects
precipitated by exercise or emotional stress, sublingual (or spray
form
1. dilation of the large veins,➔ pooling of blood in the veins ➔
↓ preload (venous return to the heart) and Afterload.
2. dilates the coronary vasculature,➔↑ blood supply to heart
↓ cardiac work➔↓ myocardial oxygen consumption
✓ onset of action varies from
1 minute nitroglycerin >1 hour Isosorbide mononitrate
✓ first-pass metabolism of nitroglycerin ➔sublingually or via a
kinetics transdermal patch
Oral isosorbide dinitrate Isosorbide mononitrate
denitration to ➔two stability against hepatic
mononitrates, (active) breakdown ➔ improved
bioavailability➔ long duration
S/E Headache. [30-60%]
postural hypotension, facial flushing, and tachycardia
| P a g e - 105 -