Page 197 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 197
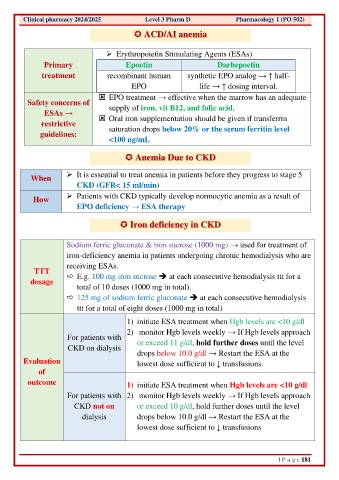
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
ACD/AI anemia
➢ Erythropoietin Stimulating Agents (ESAs)
Primary Epoetin Darbepoetin
treatment recombinant human synthetic EPO analog → ↑ half-
EPO life → ↑ dosing interval.
EPO treatment → effective when the marrow has an adequate
Safety concerns of supply of iron, vit B12, and folic acid.
ESAs →
restrictive Oral iron supplementation should be given if transferrin
saturation drops below 20% or the serum ferritin level
guidelines:
<100 ng/mL
Anemia Due to CKD
➢ It is essential to treat anemia in patients before they progress to stage 5
When
CKD (GFR< 15 ml/min)
How ➢ Patients with CKD typically develop normocytic anemia as a result of
EPO deficiency → ESA therapy
Iron deficiency in CKD
Sodium ferric gluconate & iron sucrose (1000 mg) → used for treatment of
iron-deficiency anemia in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis who are
receiving ESAs.
TTT
dosage E.g. 100 mg iron sucrose ➔ at each consecutive hemodialysis ttt for a
total of 10 doses (1000 mg in total).
125 mg of sodium ferric gluconate ➔ at each consecutive hemodialysis
ttt for a total of eight doses (1000 mg in total)
1) initiate ESA treatment when Hgb levels are <10 g/dl
2) monitor Hgb levels weekly → If Hgb levels approach
For patients with or exceed 11 g/dl, hold further doses until the level
CKD on dialysis
drops below 10.0 g/dl → Restart the ESA at the
Evaluation lowest dose sufficient to ↓ transfusions.
of
outcome 1) initiate ESA treatment when Hgb levels are <10 g/dl
For patients with 2) monitor Hgb levels weekly → If Hgb levels approach
CKD not on or exceed 10 g/dl, hold further doses until the level
dialysis drops below 10.0 g/dl → Restart the ESA at the
lowest dose sufficient to ↓ transfusions
| P a g e 181