Page 98 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 98
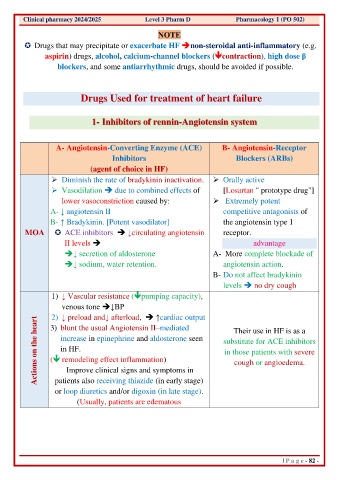
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
NOTE
Drugs that may precipitate or exacerbate HF ➔non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (e.g.
aspirin) drugs, alcohol, calcium-channel blockers (contraction), high dose β
blockers, and some antiarrhythmic drugs, should be avoided if possible.
Drugs Used for treatment of heart failure
1- Inhibitors of rennin-Angiotensin system
A- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) B- Angiotensin-Receptor
Inhibitors Blockers (ARBs)
(agent of choice in HF)
➢ Diminish the rate of bradykinin inactivation. ➢ Orally active
➢ Vasodilation ➔ due to combined effects of [Losartan " prototype drug"]
lower vasoconstriction caused by: ➢ Extremely potent
A- ↓ angiotensin II competitive antagonists of
B- ↑ Bradykinin. [Potent vasodilator] the angiotensin type 1
MOA ACE inhibitors ➔ ↓circulating angiotensin receptor.
II levels ➔ advantage
➔↓ secretion of aldosterone A- More complete blockade of
➔↓ sodium, water retention. angiotensin action.
B- Do not affect bradykinin
levels ➔ no dry cough
1) ↓ Vascular resistance (pumping capacity),
venous tone ➔↓BP
2) ↓ preload and↓ afterload, ➔ ↑cardiac output
Actions on the heart ( remodeling effect inflammation) substitute for ACE inhibitors
3) blunt the usual Angiotensin II–mediated
Their use in HF is as a
increase in epinephrine and aldosterone seen
in HF.
in those patients with severe
cough or angioedema.
Improve clinical signs and symptoms in
patients also receiving thiazide (in early stage)
or loop diuretics and/or digoxin (in late stage).
(Usually, patients are edematous
| P a g e - 82 -