Page 3 - mathematics
P. 3
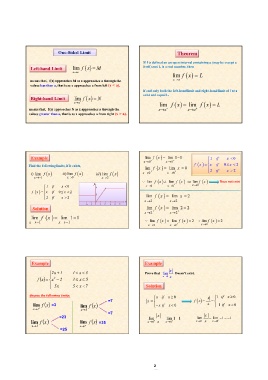
One-Sided Limit Theorem
Left-hand Limit lim f x M If f is defined on an open interval containing a (may be except a
itself) and L is a real number, then
xa
lim f x L
means that, f(x) approaches M as x approaches a through the
xa
values less than a, that is as x approaches a from left (x < a).
Right-hand Limit lim f x N if and only both the left-hand limit and right-hand limit of f at a
xa exist and equal L.
means that, f(x) approaches N as x approaches a through the lim f x lim f x L
xa xa
values greater than a, that is as x approaches a from right (x > a).
Example lim f x lim 1 1 1 if x 0
x 0 x 0 if 0x 2
f x x if
Find the following limits, if it exists, lim f x lim x 0 x 2
2
i) lim f x ii) lim f x iii) lim f x x 0 x 0
x1 x0 x2
y
x 0 lim f x lim f x lim f x Does not exist
0x 2 2 x 0 x 0 x 0
1 if
if x 2 1 lim f x lim x 2
f x x if
x 2 x 2
2 x
2 1 12 34 5 lim f x lim 2 2
Solution x 2 x 2
lim f x lim 1 1 lim f x lim f x 2 lim f x 2
x 1 x 1
x 2 x 2 x 2
Example Example
Prove that lim x Doesn’t exist.
2x 1 1 x 3
3 x5 xx 0
f x x2 2 5 x7
Solution
5x
discuss the following limits: x if x0 x 1 if x0
x if x0 x 1 if x0
lim f x =3 lim f x =7 x f x
=7
x1 x3
lim f x =23 lim f x =35 lim x lim 1 1 lim x lim 1 1
=25 x x 0 x
x5 x7 x 0 x 0 x 0
2