Page 12 - D
P. 12
Ch.6
Aerial Photogrammetry
Principles of Photogrammetry. Aerial photogrammetry enables the accurate mapping
of 3D coordinates on the ground, using 2D coordinates measured on stereo aerial
photographs that see the same points on the ground from two or more different
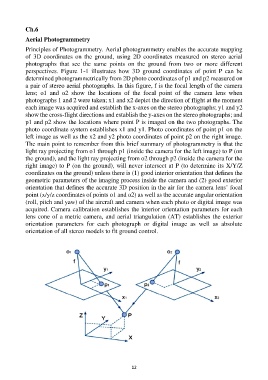
perspectives. Figure 1-1 illustrates how 3D ground coordinates of point P can be
determined photogrammetrically from 2D photo coordinates of p1 and p2 measured on
a pair of stereo aerial photographs. In this figure, f is the focal length of the camera
lens; o1 and o2 show the locations of the focal point of the camera lens when
photographs 1 and 2 were taken; x1 and x2 depict the direction of flight at the moment
each image was acquired and establish the x-axes on the stereo photographs; y1 and y2
show the cross-flight directions and establish the y-axes on the stereo photographs; and
p1 and p2 show the locations where point P is imaged on the two photographs. The
photo coordinate system establishes x1 and y1. Photo coordinates of point p1 on the
left image as well as the x2 and y2 photo coordinates of point p2 on the right image.
The main point to remember from this brief summary of photogrammetry is that the
light ray projecting from o1 through p1 (inside the camera for the left image) to P (on
the ground), and the light ray projecting from o2 through p2 (inside the camera for the
right image) to P (on the ground), will never intersect at P (to determine its X/Y/Z
coordinates on the ground) unless there is (1) good interior orientation that defines the
geometric parameters of the imaging process inside the camera and (2) good exterior
orientation that defines the accurate 3D position in the air for the camera lens’ focal
point (x/y/z coordinates of points o1 and o2) as well as the accurate angular orientation
(roll, pitch and yaw) of the aircraft and camera when each photo or digital image was
acquired. Camera calibration establishes the interior orientation parameters for each
lens cone of a metric camera, and aerial triangulation (AT) establishes the exterior
orientation parameters for each photograph or digital image as well as absolute
orientation of all stereo models to fit ground control.
12