Page 102 - phytochemistry II -pharmD general
P. 102
Steroidal Alkaloids
1. Solanum glucoalkaloids
A number of Solanum species (Solanaceae) contain some glycosidal
alkaloids which may be considered as nitrogen- containing natural products
related to the steroidal cardiac glycosides and/or the steroidal saponins in
structure.
These alkaloids contain a typical steroidal structure with an OH group at C3
like the cardiac glycoside which is involved in a glycosidic linkage with one or
more monosaccharide molecules.
Thus, these alkaloids yield upon hydrolysis a basic or nitrogen –containing
steroidal structure as well as one or more monosaccharides.
The best known of these alkaloids is solanine, isolated from Solanum
tuberosum (Potato) and S. lycopersicum (tomato).
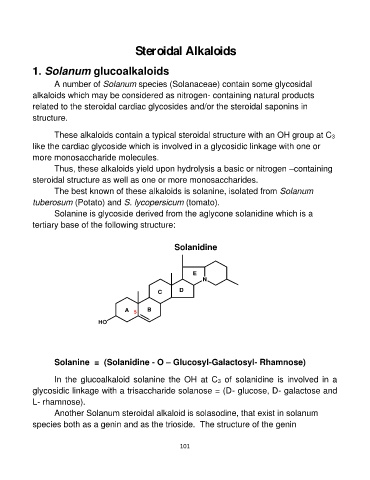
Solanine is glycoside derived from the aglycone solanidine which is a
tertiary base of the following structure:
Solanidine
E
N
CD
A5 B
HO
Solanine = (Solanidine - O – Glucosyl-Galactosyl- Rhamnose)
In the glucoalkaloid solanine the OH at C3 of solanidine is involved in a
glycosidic linkage with a trisaccharide solanose = (D- glucose, D- galactose and
L- rhamnose).
Another Solanum steroidal alkaloid is solasodine, that exist in solanum
species both as a genin and as the trioside. The structure of the genin
101