Page 6 - Pharmaceutics III_ 02-06-01304_Fall 2025_ Pharm D_Electronic book
P. 6
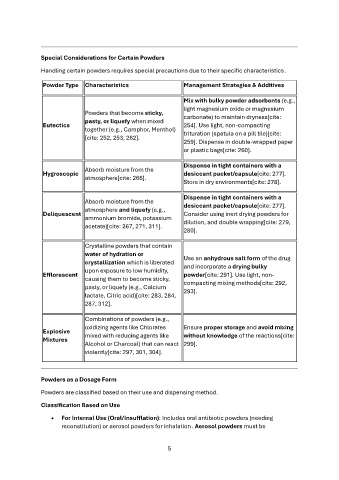
Special Considerations for Certain Powders
Handling certain powders requires special precautions due to their specific characteristics .
Powder Type Characteristics Management Strategies & Additives
Eutectics Powders that become sticky, Mix with bulky powder adsorbents (e.g.,
pasty, or liquefy when mixed light magnesium oxide or magnesium
together (e.g., Camphor, Menthol) carbonate) to maintain dryness[cite:
[cite: 252, 253, 262]. 254]. Use light, non-compacting
trituration (spatula on a pill tile)[cite:
259]. Dispense in double-wrapped paper
or plastic bags[cite: 260].
Hygroscopic Absorb moisture from the Dispense in tight containers with a
atmosphere[cite: 266]. desiccant packet/capsule[cite: 277].
Store in dry environments[cite: 278].
Absorb moisture from the Dispense in tight containers with a
desiccant packet/capsule[cite: 277].
Deliquescent atmosphere and liquefy (e.g., Consider using inert drying powders for
ammonium bromide, potassium dilution, and double wrapping[cite: 279,
280].
acetate)[cite: 267, 271, 311].
Efflorescent Crystalline powders that contain Use an anhydrous salt form of the drug
water of hydration or and incorporate a drying bulky
crystallization which is liberated powder[cite: 291]. Use light, non-
upon exposure to low humidity, compacting mixing methods[cite: 292,
causing them to become sticky, 293].
pasty, or liquefy (e.g., Calcium
lactate, Citric acid)[cite: 283, 284,
287, 312].
Combinations of powders (e.g.,
Explosive oxidizing agents like Chlorates Ensure proper storage and avoid mixing
Mixtures
mixed with reducing agents like without knowledge of the reactions[cite:
Alcohol or Charcoal) that can react 299].
violently[cite: 297, 301, 304].
Powders as a Dosage Form
Powders are classified based on their use and dispensing method.
Classification Based on Use
• For Internal Use (Oral/Insufflation): Includes oral antibiotic powders (needing
reconstitution) or aerosol powders for inhalation . Aerosol powders must be
5