Page 9 - Pharmaceutics III_ 02-06-01304_Fall 2025_ Pharm D_Electronic book
P. 9
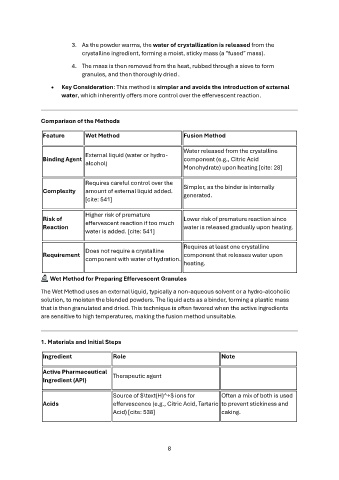
3. As the powder warms, the water of crystallization is released from the
crystalline ingredient, forming a moist, sticky mass (a "fused" mass).
4. The mass is then removed from the heat, rubbed through a sieve to form
granules, and then thoroughly dried .
• Key Consideration: This method is simpler and avoids the introduction of external
water, which inherently offers more control over the effervescent reaction.
Comparison of the Methods
Feature Wet Method Fusion Method
Binding Agent External liquid (water or hydro- Water released from the crystalline
alcohol) component (e.g., Citric Acid
Monohydrate) upon heating [cite: 28]
Complexity Requires careful control over the Simpler, as the binder is internally
amount of external liquid added. generated.
[cite: 541]
Risk of Higher risk of premature Lower risk of premature reaction since
Reaction effervescent reaction if too much water is released gradually upon heating.
water is added. [cite: 541]
Requirement Does not require a crystalline Requires at least one crystalline
component with water of hydration. component that releases water upon
heating.
Wet Method for Preparing Effervescent Granules
The Wet Method uses an external liquid, typically a non-aqueous solvent or a hydro-alcoholic
solution, to moisten the blended powders. The liquid acts as a binder, forming a plastic mass
that is then granulated and dried. This technique is often favored when the active ingredients
are sensitive to high temperatures, making the fusion method unsuitable.
1. Materials and Initial Steps
Ingredient Role Note
Active Pharmaceutical Therapeutic agent
Ingredient (API)
Source of $\text{H}^+$ ions for Often a mix of both is used
Acids effervescence (e.g., Citric Acid, Tartaric to prevent stickiness and
Acid) [cite: 538] caking.
8