Page 126 - Pharm.Org.Chem-I 02-06-05-101
P. 126
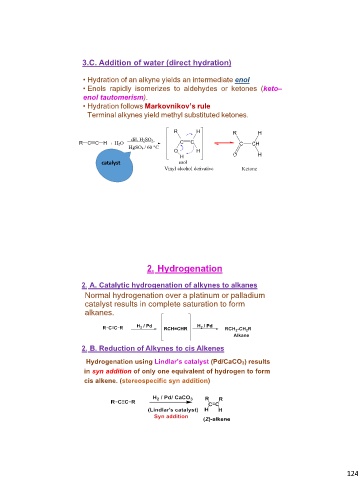
3.C. Addition of water (direct hydration)
• Hydration of an alkyne yields an intermediate enol.
• Enols rapidly isomerizes to aldehydes or ketones (keto–
enol tautomerism).
• Hydration follows Markovnikov’s rule
Terminal alkynes yield methyl substituted ketones.
RH
R C C H + H2O dil. H2SO4 CC
HgSO4 / 60 °C OH
H
enol
catalyst
Vinyl alcohol derivative
2. Hydrogenation
2. A. Catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes to alkanes
Normal hydrogenation over a platinum or palladium
catalyst results in complete saturation to form
alkanes.
2. B. Reduction of Alkynes to cis Alkenes
Hydrogenation using Lindlar’s catalyst (Pd/CaCO3) results
in syn addition of only one equivalent of hydrogen to form
cis alkene. (stereospecific syn addition)
124