Page 126 - Pharmd general phytochemistry I-Final2024_LEUCTERS
P. 126
Side effects:
The undesirable side effects particularly oto- and nephrotoxicity, restricted their
systemic use.
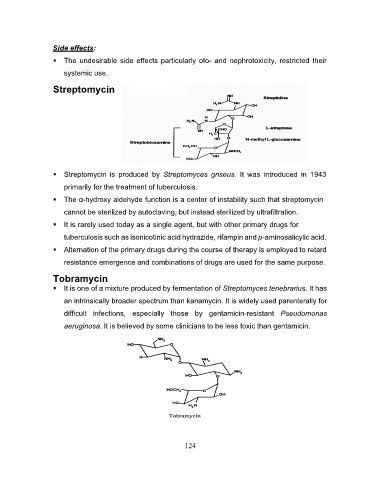
Streptomycin
Streptomycin is produced by Streptomyces griseus. It was introduced in 1943
primarily for the treatment of tuberculosis.
The α-hydroxy aldehyde function is a center of instability such that streptomycin
cannot be sterilized by autoclaving, but instead sterilized by ultrafiltration.
It is rarely used today as a single agent, but with other primary drugs for
tuberculosis such as isonicotinic acid hydrazide, rifampin and p-aminosalicylic acid.
Alternation of the primary drugs during the course of therapy is employed to retard
resistance emergence and combinations of drugs are used for the same purpose.
Tobramycin
It is one of a mixture produced by fermentation of Streptomyces tenebrarius. It has
an intrinsically broader spectrum than kanamycin. It is widely used parenterally for
difficult infections, especially those by gentamicin-resistant Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. It is believed by some clinicians to be less toxic than gentamicin.
124