Page 36 - The Homeowner's Handbook 2017
P. 36
THE HOMEOWNER’S HANDBOOK EIGHTH EDITION
A Breakdown on High-Performance Windows
INDOWS ARE AN IMPORTANT FACTOR in coatings, which can reduce energy loss by 30 percent to 50 percent,
improving the performance of the building according to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). Some windows
envelope. But with so many options available, are tinted or coated with heat-absorbing glazing, which absorbs
selecting the right window can be challenging. solar radiation and reduces the solar heat gain coefficient, visible
To increase insulation, homeowners should transmittance and glare.
W choose a double- or triple-pane window. Storm windows are another option for efficient windows. Though they
Between each pane is an insulating air pocket, so more panes means don’t add more insulation, but they can help reduce the amount of air
more insulation. These windows can be filled with gases such as argon flow through windows, which can help with heating and cooling costs.
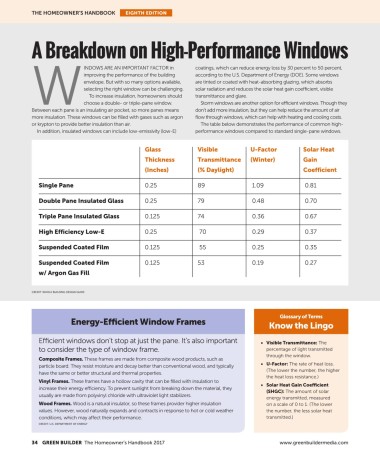
or krypton to provide better insulation than air. The table below demonstrates the performance of common high-
In addition, insulated windows can include low-emissivity (low-E) performance windows compared to standard single-pane windows.
Glass Visible U-Factor Solar Heat
Thickness Transmittance (Winter) Gain
(Inches) (% Daylight) Coefficient
Single Pane 0.25 89 1.09 0.81
Double Pane Insulated Glass 0.25 79 0.48 0.70
Triple Pane Insulated Glass 0.125 74 0.36 0.67
High Efficiency Low-E 0.25 70 0.29 0.37
Suspended Coated Film 0.125 55 0.25 0.35
Suspended Coated Film 0.125 53 0.19 0.27
w/ Argon Gas Fill
CREDIT: WHOLE BUILDING DESIGN GUIDE
Glossary of Terms
Energy-Efficient Window Frames Know the Lingo
Efficient windows don’t stop at just the pane. It’s also important ■ ■ Visible Transmittance: The
to consider the type of window frame. percentage of light transmitted
through the window.
Composite Frames. These frames are made from composite wood products, such as
particle board. They resist moisture and decay better than conventional wood, and typically ■ ■ U-Factor: The rate of heat loss.
(The lower the number, the higher
have the same or better structural and thermal properties.
the heat loss resistance.)
Vinyl Frames. These frames have a hollow cavity that can be filled with insulation to
■ ■ Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
increase their energy efficiency. To prevent sunlight from breaking down the material, they
(SHGC): The amount of solar
usually are made from polyvinyl chloride with ultraviolet light stabilizers.
energy transmitted, measured
Wood Frames. Wood is a natural insulator, so these frames provider higher insulation on a scale of 0 to 1. (The lower
values. However, wood naturally expands and contracts in response to hot or cold weather the number, the less solar heat
conditions, which may affect their performance. transmitted.)
CREDIT: U.S. DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
34 GREEN BUILDER The Homeowner’s Handbook 2017 www.greenbuildermedia.com
9-61 GB 1017 HH.indd 34 11/1/17 12:08 PM