Page 58 - 4. Pre-Course Reading-Training on Forestry Audit 2019
P. 58
Auditing Forests: Guidance for Supreme Audit Institutions
RESEARCHABLE RESEARCHABLE
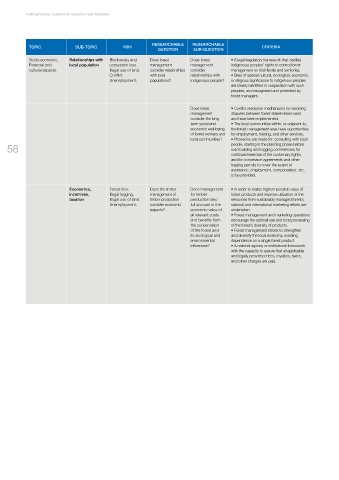
TOPIC SUB-TOPIC RSIK CRITERIA
QUESTION SUB-QUESTION
Socio-economic, Relationships with Biodiversity and Does forest Does forest • A legal/regulatory framework that clarifies
Financial and local population ecosystem loss. management management indigenous peoples’ rights to control forest
cultural aspects. Illegal use of land. consider relationships consider management on their lands and territories.
Conflict. with local relationships with • Sites of special cultural, ecological, economic,
Unemployment. populations? indigenous people? or religious significance to indigenous peoples
are clearly identified in cooperation with such
peoples, and recognized and protected by
forest managers.
Does forest • Conflict resolution mechanisms for resolving
management disputes between forest stakeholders exist
consider the long and have been implemented.
term social and • The local communities within, or adjacent to,
economic well-being the forest management area have opportunities
of forest workers and for employment, training, and other services.
local communities? • Provisions are made for: consulting with local
58 people, starting in the planning phase before
road building and logging commences; for
continued exercise of the customary rights;
and for concession agreements and other
logging permits to cover the extent of
assistance, employment, compensation, etc.,
to be provided.
Economics, Forest fires. Does the timber Does management • In order to realize highest possible value of
incentives, Illegal logging. management of for timber forest products and improve utilization of the
taxation Illegal use of land. timber production production take resources from sustainably managed forests,
Unemployment. consider economic full account in the national and international marketing efforts are
aspects? economic value of undertaken.
all relevant costs • Forest management and marketing operations
and benefits from encourage the optimal use and local processing
the conservation of the forest’s diversity of products.
of the forest and • Forest management strives to strengthen
its ecological and and diversify the local economy, avoiding
environmental dependence on a single forest product.
influences? • A national agency or institutional framework
with the capacity to assure that all applicable
and legally prescribed fees, royalties, taxes,
and other charges are paid.