Page 46 - The Miraculous Machine that Works for an Entire Lifetime: Enzyme
P. 46
Harun Yahya
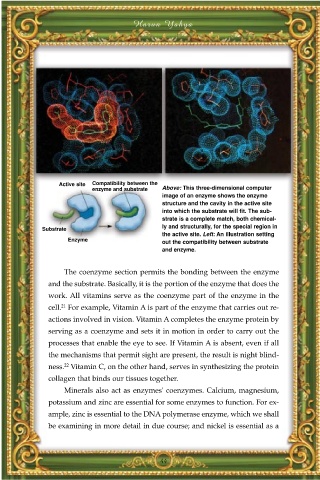
Active site Compatibility between the
enzyme and substrate Above: This three-dimensional computer
image of an enzyme shows the enzyme
structure and the cavity in the active site
into which the substrate will fit. The sub-
strate is a complete match, both chemical-
ly and structurally, for the special region in
Substrate
the active site. Left: An illustration setting
Enzyme out the compatibility between substrate
and enzyme.
The coenzyme section permits the bonding between the enzyme
and the substrate. Basically, it is the portion of the enzyme that does the
work. All vitamins serve as the coenzyme part of the enzyme in the
cell. For example, Vitamin A is part of the enzyme that carries out re-
21
actions involved in vision. Vitamin A completes the enzyme protein by
serving as a coenzyme and sets it in motion in order to carry out the
processes that enable the eye to see. If Vitamin A is absent, even if all
the mechanisms that permit sight are present, the result is night blind-
22
ness. Vitamin C, on the other hand, serves in synthesizing the protein
collagen that binds our tissues together.
Minerals also act as enzymes' coenzymes. Calcium, magnesium,
potassium and zinc are essential for some enzymes to function. For ex-
ample, zinc is essential to the DNA polymerase enzyme, which we shall
be examining in more detail in due course; and nickel is essential as a
44