Page 33 - The Miracle of Creation in DNA
P. 33
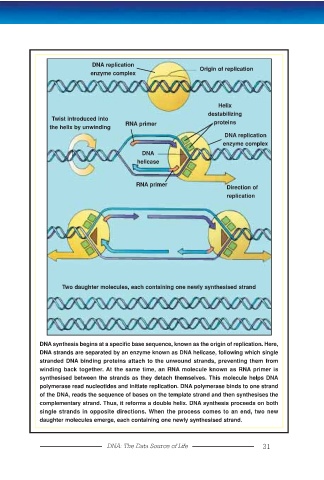
DNA replication
Origin of replication
Origin of replication
enzyme complex
Helix
destabilizing
Twist introduced into
RNA primer proteins
the helix by unwinding
DNA replication
enzyme complex
DNA
helicase
RNA primer
Direction of
replication
Two daughter molecules, each containing one newly synthesised strand
DNA synthesis begins at a specific base sequence, known as the origin of replication. Here,
DNA strands are separated by an enzyme known as DNA helicase, following which single
stranded DNA binding proteins attach to the unwound strands, preventing them from
winding back together. At the same time, an RNA molecule known as RNA primer is
synthesised between the strands as they detach themselves. This molecule helps DNA
polymerase read nucleotides and initiate replication. DNA polymerase binds to one strand
of the DNA, reads the sequence of bases on the template strand and then synthesises the
complementary strand. Thus, it reforms a double helix. DNA synthesis proceeds on both
single strands in opposite directions. When the process comes to an end, two new
daughter molecules emerge, each containing one newly synthesised strand.
DNA: The Data Source of Life 31