Page 57 - The prevalence of the Val66Met polymorphism in musicians: Possible evidence for compensatory neuroplasticity from a pilot study
P. 57
S. Si et al. NeuroImage 213 (2020) 116681
2.3. Statistical analysis Table 2
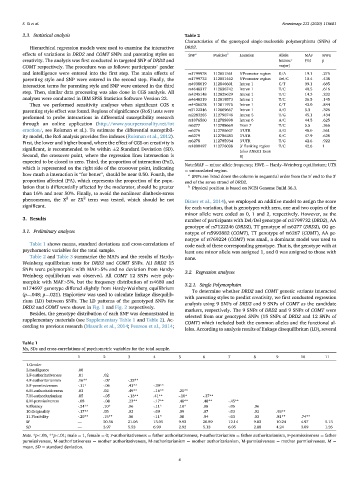
Characteristics of the genotyped single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of
Hierarchical regression models were used to examine the interactive DRD2.
effects of variations in DRD2 and COMT SNPs and parenting styles on SNP a Position b Location Allele MAF HWE
creativity. The analysis was first conducted in targeted SNP of DRD2 and (minor/ (%) p
COMT respectively. The procedure was as follows: participants’ gender major)
and intelligence were entered into the first step. The main effects of rs1799978 112851561 5 Promoter region G/A 19.1 .275
0
0
parenting style and SNP were entered in the second step. Finally, the rs1799732 112851462 5 Promoter region Del/C 10.4 .438
rs4938019 112846601 Intron 1 C/T 39.1 .685
interaction terms for parenting style and SNP were entered in the third
rs4648317 112836742 Intron 1 T/C 40.5 .616
step. Then, similar data processing was also done in CGS analysis. All
rs4245148 112825629 Intron 1 T/C 14.3 .232
analyses were conducted in IBM SPSS Statistics Software Version 22. rs4648319 112819573 Intron 1 T/C 36.5 .145
Then we performed sensitivity analyses when significant CGS x rs4436578 112811975 Intron 1 C/T 43.0 .844
parenting style effect was found. Regions of significance (RoS) tests were rs7122246 112809667 Intron 1 A/G 5.3 .326
rs2283265 112790746 Intron 5 T/G 45.1 .434
performed to probe interactions in differential susceptibility research
rs1076560 112788898 Intron 6 A/C 44.5 .625
through an online application (http://www.yourpersonality.net/int rs6277 112788669 Exon 7 T/C 5.5 .366
eraction/, see Roisman et al.). To estimate the differential susceptibil- rs6276 112786607 3 UTR A/G 48.0 .561
0
ity model, the RoS analysis provides five indexes (Roisman et al., 2012). rs6279 112786283 3 UTR G/C 47.9 .628
0
rs6278 112785934 3 UTR T/G 42.6 .922
0
First, the lower and higher bound, where the effect of CGS on creativity is
rs1800497 112776038 3 flanking region T/C 42.6 1
0
significant, is recommended to be within 2 Standard Deviation (SD).
(also ANKK1 Exon
Second, the crossover point, where the regression lines intersection is 8)
expected to be closed to zero. Third, the proportion of interaction (PoI),
Note:MAF ¼ minor allele frequency; HWE ¼ Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium; UTR
which is represented on the right side of the crossover point, indicating
¼ untranslated region.
how much a interaction is “for better”, should be near 0.50. Fourth, the a
0
SNPs are listed down the column in sequential order from the 5 end to the 3 0
proportion affected (PA), which represents the proportion of the popu- end of the sense strand of DRD2.
lation that is differentially affected by the moderator, should be greater b Physical position is based on NCBI Genome Build 36.3.
than 16% and near 50%. Finally, to avoid the nonlinear diathesis-stress
2
2
phenomenon, the X or ZX term was tested, which should be not Disner et al., 2014), we employed an additive model to assign the score
significant. for each variation, that is genotypes with zero, one and two copies of the
minor allele were coded as 0, 1 and 2, respectively. However, as the
3. Results number of participants with Del/Del genotype of rs1799732 (DRD2), AA
genotype of rs7122246 (DRD2), TT genotype of rs6277 (DRD2), GG ge-
3.1. Preliminary analyses notype of rs5993882 (COMT), TT genotype of rs6267 (COMT), AA ge-
notype of rs769224 (COMT) was small, a dominant model was used to
Table 1 shows means, standard deviations and cross-correlations of code each of these corresponding genotype. That is, the genotype with at
psychometric variables for the total sample. least one minor allele was assigned 1, and 0 was assigned to those with
Table 2 and Table 3 summarize the MAFs and the results of Hardy- none.
Weinberg equilibrium tests for DRD2 and COMT SNPs. All DRD2 15
SNPs were polymorphic with MAF>5% and no deviation from Hardy- 3.2. Regression analyses
Weinberg equilibrium was observed. All COMT 12 SNPs were poly-
morphic with MAF>5%, but the frequency distribution of rs4680 and 3.2.1. Single Polymorphsim
rs174697 genotype differed slightly from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
To determine whether DRD2 and COMT genetic variants interacted
(p¼.048; p¼.021). Haploview was used to calculate linkage disequilib-
with parenting styles to predict creativity, we first conducted regression
rium (LD) between SNPs. The LD patterns of the genotyped SNPs for
analysis using 9 SNPs of DRD2 and 9 SNPs of COMT as the candidate
DRD2 and COMT were shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 respectively.
markers, respectively. The 9 SNPs of DRD2 and 9 SNPs of COMT were
Besides, the genotype distribution of each SNP was demonstrated in
selected from our genotyped SNPs (15 SNPs of DRD2 and 12 SNPs of
supplementary materials (see Supplementary Table 1 and Table 2). Ac- COMT) which included both the common alleles and the functional al-
cording to previous research (Masarik et al., 2014; Pearson et al., 2014;
leles. According to analysis results of linkage disequilibrium (LD), several
Table 1
Ms, SDs and cross-correlations of psychometric variables for the total sample.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
1.Gender
2.Intelligence .00
3.F-authoritativeness .01 .02
4.F-authoritarianism .16** -.07 -.33**
5.F-permissiveness -.11* -.06 .41** -.39**
6.M-authoritativeness .03 .02 .49** -.16** .21**
7.M-authoritarianism .05 -.05 -.13** .41** -.10* -.37**
8.M-permissiveness -.08 -.08 .23** -.17** .48** .48** -.45**
9.Fluency -.24** .10* .06 -.11* .10* .08 -.05 .06
10.Originality -.17** .05 .03 -.09 .09 .07 -.03 .02 .93**
11.Flexibility -.20** .15** .06 -.11* .08 .04 -.03 .03 .81** .74**
M — 20.56 21.06 13.05 9.92 20.89 12.14 9.82 10.24 4.97 5.13
SD — 3.97 5.53 6.99 2.92 5.13 6.05 2.88 4.24 3.09 1.26
Note.*p<.05, **p<.01; male ¼ 1, female ¼ 0; F-authoritativeness ¼ father authoritativeness, F-authoritarianism ¼ father authoritarianism, F-permissiveness ¼ father
permissiveness, M-authoritativeness ¼ mother authoritativeness, M-authoritarianism ¼ mother authoritarianism, M-permissiveness ¼ mother permissiveness. M ¼
mean, SD ¼ standard deviation.
4