Page 58 - The prevalence of the Val66Met polymorphism in musicians: Possible evidence for compensatory neuroplasticity from a pilot study
P. 58
S. Si et al. NeuroImage 213 (2020) 116681
Table 3 only one of each of them was included in single variants parenting style
Characteristics of the genotyped single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of analysis. rs1800497, rs6276, rs6277, rs2283265, rs1076560 and
COMT. rs4938019 were excluded. For COMT, strong LDs were observed for
2
2
SNP Position Location Allele (minor/ MAF HWE p rs6269 and rs4646312 (r ¼.92), rs4818 and rs4646312 (r ¼.92), rs4818
2
2
major) (%) and rs6269 (r ¼.92), rs4633 and rs4680 (r ¼.92). Hence, rs4646312,
rs737865 18310121 Intron 1 C/T 29.7 .907 rs4818 and rs4680 were excluded. Finally, 9 SNPs of DRD2 (rs6278,
rs174675 18314051 Intron 1 T/C 39.3 .612 rs6279, rs7122246, rs4648317, rs1799978, rs1799732, rs4245148,
rs5993882 18317533 Intron 1 G/T 12.1 1 rs4648319, rs4436578) and 9 SNPs of COMT (rs6269, rs4633, rs737865,
rs5993883 18317638 Intron 1 G/T 41.3 .690 rs174675, rs5993882, rs5993883, rs6267, rs769224, rs174697) were
rs4646312 18328337 Intron 1 C/T 37.6 .217
rs6269 18329952 Exon 3 G/A 37.9 .182 selected to conduct single variants parenting style analysis.
rs4633 18330235 Exon 3 T/C 26.2 .104 To minimize the likelihood of a Type I error, we adjusted our alpha
rs6267 18330263 Exon 3 T/G 7.5 .721 based on the number of genetic polymorphisms we planned to examine in
rs4818 18331207 Exon 4 G/C 37.2 .254 a gene. Given that we are investigating nine polymorphisms in each gene,
rs4680 18331271 Exon 4 A/G 26.6 .048* we used a conservative Bonferroni adjusted alpha of .006 (a ¼ .05/9) to
rs769224 18331804 Exon 5 A/G 6.9 .710
rs174697 18333832 Intron 5 A/G 32.9 .021* determine statistical significance.
The significant results for each model testing the individual variant
Note:*p<.05; MAF ¼ minor allele frequency; HWE ¼ Hardy-Weinberg equilib- parenting style interactions for the prediction of fluency, originality and
rium; UTR ¼ untranslated region.
a 0 0 flexibility are shown in supplementary materials (Supplementary Table 3
SNPs are listed down the column in sequential order from the 5 end to the 3 end
of the sense strand of COMT. and Table 4). While neither single polymorphism nor parenting style was
b Physical position is based on NCBI Genome Build 36.3. independently significant in the model including rs5993882 and
rs5993883, the two-way interaction term of mother authoritativeness
SNPs were excluded in single variants parenting style analysis because and COMT genotype, controlling for participant gender and intelligence,
was significant in predicting creativity (fluency: β ¼ 0.14, p ¼ 0.002;
of their strong LDs with other SNPs. For DRD2, strong LDs were observed
2
2
for rs6278 and rs1800497 (r ¼.97), rs6276 and rs6279 (r ¼.99), rs6277 flexibility: β ¼ 0.14, p ¼ 0.004). However, none of the models including
2
2
and rs7122246 (r ¼.91), rs2283265 and rs1076560 (r ¼.97), rs1076560 other polymorphisms in DRD2 and COMT passed the Bonferroni adjusted
2
2
and rs6278 (r ¼.90), rs4938019 and rs4648317 (r ¼.92). Therefore, threshold (p < 0.006) for statistical significance though there were seven
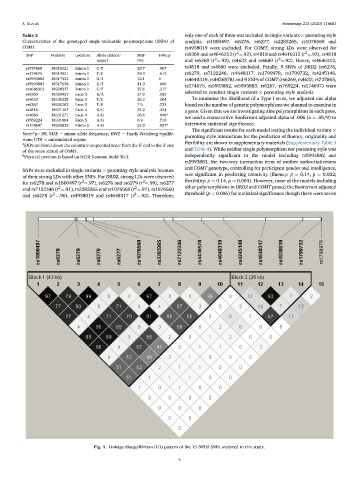
Fig. 1. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) pattern of the 15 DRD2 SNPs analyzed in this study.
5