Page 4 - Prueba
P. 4
2 Eyes and vision
Eyes detect light stimuli. Most of the eye is situated within the eye socket GLOSSARY
and protected by the cranium. It is divided into two sections: the anterior decipher: to interpret the meaning
and posterior cavities. The eye is made up of three layers: the sclera, the
choroid and the retina.
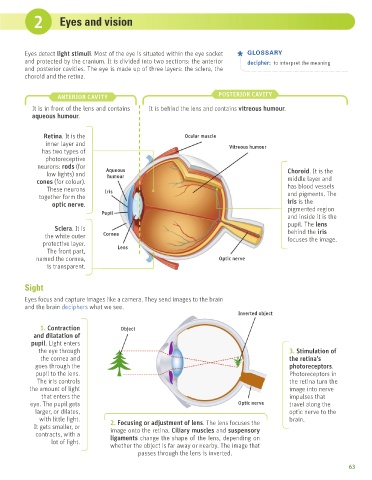
ANTERIOR CAVITY POSTERIOR CAVITY
It is in front of the lens and contains It is behind the lens and contains vitreous humour.
aqueous humour.
Retina. It is the Ocular muscle
inner layer and Vitreous humour
has two types of
photoreceptive
neurons: rods (for Aqueous
low lights) and humour Choroid. It is the
cones (for colour). middle layer and
These neurons Iris has blood vessels
together form the and pigments. The
optic nerve. iris is the
Pupil pigmented region
and inside it is the
pupil. The lens
Sclera. It is behind the iris
the white outer Cornea focuses the image.
protective layer. Lens
The front part,
named the cornea, Optic nerve
is transparent.
Sight
Eyes focus and capture images like a camera. They send images to the brain
and the brain deciphers what we see.
Inverted object
1. Contraction Object
and dilatation of
pupil. Light enters
the eye through 3. Stimulation of
the cornea and the retina’s
goes through the photoreceptors.
pupil to the lens. Photoreceptors in
The iris controls the retina turn the
the amount of light image into nerve
that enters the impulses that
eye. The pupil gets Optic nerve travel along the
larger, or dilates, optic nerve to the
with little light. 2. Focusing or adjustment of lens. The lens focuses the brain.
It gets smaller, or image onto the retina. Ciliary muscles and suspensory
contracts, with a ligaments change the shape of the lens, depending on
lot of light.
whether the object is far away or nearby. The image that
passes through the lens is inverted.
63