Page 5 - Prueba
P. 5
3 Ears: balance and hearing
GLOSSARY Our ears capture sound waves. They also give us information about our
feature: a prominent characteristic movements, balance and position. The ear can be divided into three parts:
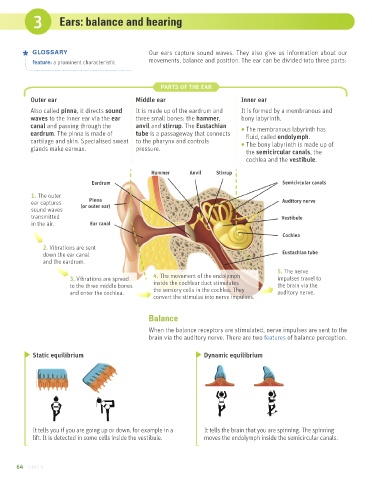
PARTS OF THE EAR
Outer ear Middle ear Inner ear
Also called pinna, it directs sound It is made up of the eardrum and It is formed by a membranous and
waves to the inner ear via the ear three small bones: the hammer, bony labyrinth.
canal and passing through the anvil and stirrup. The Eustachian
eardrum. The pinna is made of tube is a passageway that connects • The membranous labyrinth has
fluid, called endolymph.
cartilage and skin. Specialised sweat to the pharynx and controls
glands make earwax. pressure. • The bony labyrinth is made up of
the semicircular canals, the
cochlea and the vestibule.
Hammer Anvil Stirrup
Eardrum Semicircular canals
1. The outer
ear captures Pinna Auditory nerve
sound waves (or outer ear)
transmitted Vestibule
in the air. Ear canal
Cochlea
2. Vibrations are sent
down the ear canal Eustachian tube
and the eardrum.
5. The nerve
3. Vibrations are spread 4. The movement of the endolymph impulses travel to
to the three middle bones inside the cochlear duct stimulates the brain via the
and enter the cochlea. the sensory cells in the cochlea. They auditory nerve.
convert the stimulus into nerve impulses.
Balance
When the balance receptors are stimulated, nerve impulses are sent to the
brain via the auditory nerve. There are two features of balance perception.
Static equilibrium Dynamic equilibrium
It tells you if you are going up or down, for example in a It tells the brain that you are spinning. The spinning
lift. It is detected in some cells inside the vestibule. moves the endolymph inside the semicircular canals.
64 UNIT 6