Page 25 - Practical-workbook-organic-3
P. 25
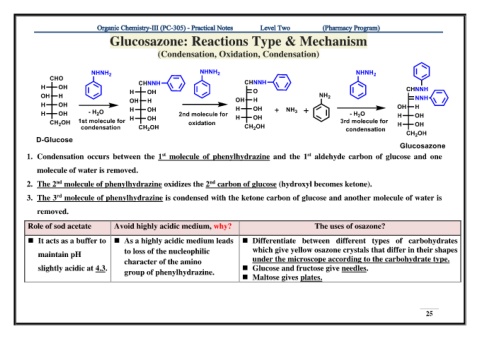
Glucosazone: Reactions Type & Mechanism
(Condensation, Oxidation, Condensation)
st
st
1. Condensation occurs between the 1 molecule of phenylhydrazine and the 1 aldehyde carbon of glucose and one
molecule of water is removed.
nd
nd
2. The 2 molecule of phenylhydrazine oxidizes the 2 carbon of glucose (hydroxyl becomes ketone).
rd
3. The 3 molecule of phenylhydrazine is condensed with the ketone carbon of glucose and another molecule of water is
removed.
Role of sod acetate Avoid highly acidic medium, why? The uses of osazone?
◼ It acts as a buffer to ◼ As a highly acidic medium leads ◼ Differentiate between different types of carbohydrates
maintain pH to loss of the nucleophilic which give yellow osazone crystals that differ in their shapes
character of the amino under the microscope according to the carbohydrate type.
slightly acidic at 4.3. ◼ Glucose and fructose give needles.
group of phenylhydrazine.
◼ Maltose gives plates.
25