Page 127 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 127
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
Precautions of Mohr’s Method
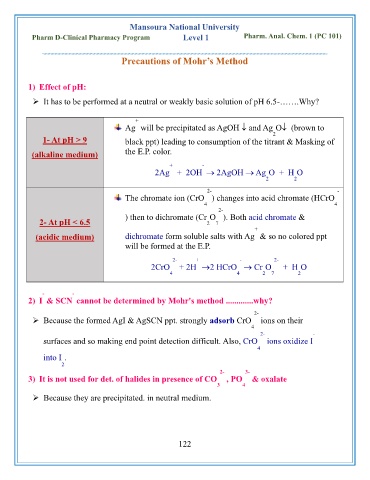
1) Effect of pH:
➢ It has to be performed at a neutral or weakly basic solution of pH 6.5-…….Why?
+
Ag will be precipitated as AgOH and Ag O (brown to
2
1- At pH > 9 black ppt) leading to consumption of the titrant & Masking of
(alkaline medium) the E.P. color.
+ -
2Ag + 2OH → 2AgOH → Ag O + H O
2 2
2- -
The chromate ion (CrO ) changes into acid chromate (HCrO
4 4
2-
) then to dichromate (Cr O ). Both acid chromate &
2- At pH < 6.5 2 7
+
(acidic medium) dichromate form soluble salts with Ag & so no colored ppt
will be formed at the E.P.
2- + - 2-
2CrO + 2H →2 HCrO → Cr O + H O
4 4 2 7 2
- -
2) I & SCN cannot be determined by Mohr's method .............why?
2-
➢ Because the formed AgI & AgSCN ppt. strongly adsorb CrO ions on their
4
2- -
surfaces and so making end point detection difficult. Also, CrO ions oxidize I
4
into I .
2
2- 3-
3) It is not used for det. of halides in presence of CO , PO & oxalate
3 4
➢ Because they are precipitated. in neutral medium.
122