Page 16 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 16
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
Concentration Units
➢ There are numerous ways of expressing the concentration of a solution, from which
we will study only two:
I. Molarity (M)
II. Normality (N)
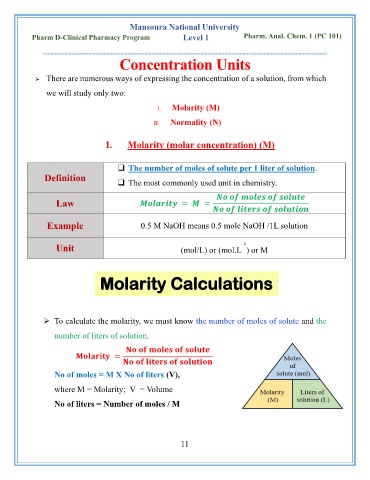
I. Molarity (molar concentration) (M)
❑ The number of moles of solute per 1 liter of solution.
Definition
❑ The most commonly used unit in chemistry.
Law = =
Example 0.5 M NaOH means 0.5 mole NaOH /1L solution
-1
Unit (mol/L) or (mol.L ) or M
Molarity Calculations
➢ To calculate the molarity, we must know the number of moles of solute and the
number of liters of solution.
=
No of moles = M X No of liters (V),
where M = Molarity; V = Volume
No of liters = Number of moles / M
11