Page 21 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 21
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
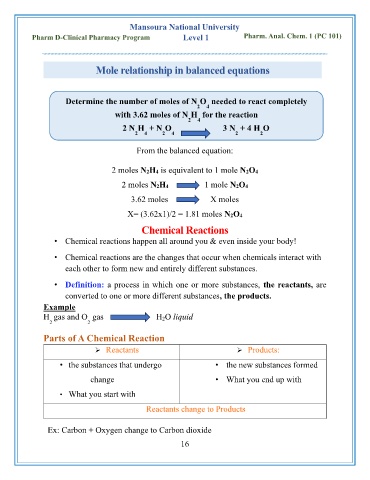
Mole relationship in balanced equations
Determine the number of moles of N O needed to react completely
2
4
with 3.62 moles of N H for the reaction
2 4
2 N H + N O 3 N + 4 H O
2 4 2 4 2 2
From the balanced equation:
2 moles N2H4 is equivalent to 1 mole N2O4
2 moles N2H4 1 mole N2O4
3.62 moles X moles
X= (3.62x1)/2 = 1.81 moles N2O4
Chemical Reactions
• Chemical reactions happen all around you & even inside your body!
• Chemical reactions are the changes that occur when chemicals interact with
each other to form new and entirely different substances.
• Definition: a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are
converted to one or more different substances, the products.
Example
H gas and O gas H 2O liquid
2 2
Parts of A Chemical Reaction
➢ Reactants ➢ Products:
• the substances that undergo • the new substances formed
change • What you end up with
• What you start with
Reactants change to Products
Ex: Carbon + Oxygen change to Carbon dioxide
16