Page 26 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 26
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
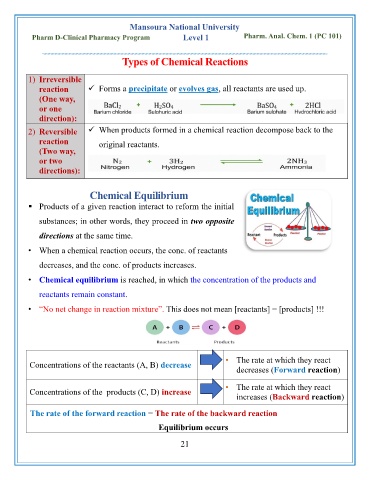
Types of Chemical Reactions
1) Irreversible
reaction ✓ Forms a precipitate or evolves gas, all reactants are used up.
(One way,
or one
direction):
2) Reversible ✓ When products formed in a chemical reaction decompose back to the
reaction original reactants.
(Two way,
or two
directions):
Chemical Equilibrium
▪ Products of a given reaction interact to reform the initial
substances; in other words, they proceed in two opposite
directions at the same time.
• When a chemical reaction occurs, the conc. of reactants
decreases, and the conc. of products increases.
• Chemical equilibrium is reached, in which the concentration of the products and
reactants remain constant.
• “No net change in reaction mixture”. This does not mean [reactants] = [products] !!!
• The rate at which they react
Concentrations of the reactants (A, B) decrease
decreases (Forward reaction)
• The rate at which they react
Concentrations of the products (C, D) increase
increases (Backward reaction)
The rate of the forward reaction = The rate of the backward reaction
Equilibrium occurs
21