Page 104 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 104
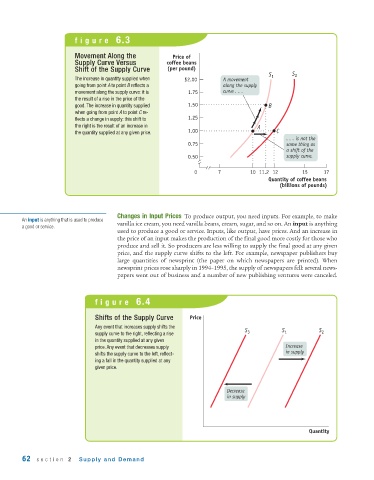
figure 6.3
Movement Along the Price of
Supply Curve Versus coffee beans
Shift of the Supply Curve (per pound)
S 1 S 2
The increase in quantity supplied when $2.00 A movement
going from point A to point B reflects a along the supply
movement along the supply curve: it is 1.75 curve . . .
the result of a rise in the price of the
good. The increase in quantity supplied 1.50 B
when going from point A to point C re-
flects a change in supply: this shift to 1.25
the right is the result of an increase in A
the quantity supplied at any given price. 1.00 C
. . . is not the
0.75 same thing as
a shift of the
0.50 supply curve.
0 7 10 11.2 12 15 17
Quantity of coffee beans
(billions of pounds)
Changes in Input Prices To produce output, you need inputs. For example, to make
An input is anything that is used to produce
a good or service. vanilla ice cream, you need vanilla beans, cream, sugar, and so on. An input is anything
used to produce a good or service. Inputs, like output, have prices. And an increase in
the price of an input makes the production of the final good more costly for those who
produce and sell it. So producers are less willing to supply the final good at any given
price, and the supply curve shifts to the left. For example, newspaper publishers buy
large quantities of newsprint (the paper on which newspapers are printed). When
newsprint prices rose sharply in 1994–1995, the supply of newspapers fell: several news-
papers went out of business and a number of new publishing ventures were canceled.
figure 6.4
Shifts of the Supply Curve Price
Any event that increases supply shifts the
S 3 S 1 S 2
supply curve to the right, reflecting a rise
in the quantity supplied at any given
price. Any event that decreases supply Increase
shifts the supply curve to the left, reflect- in supply
ing a fall in the quantity supplied at any
given price.
Decrease
in supply
Quantity
62 section 2 Supply and Demand