Page 384 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 384
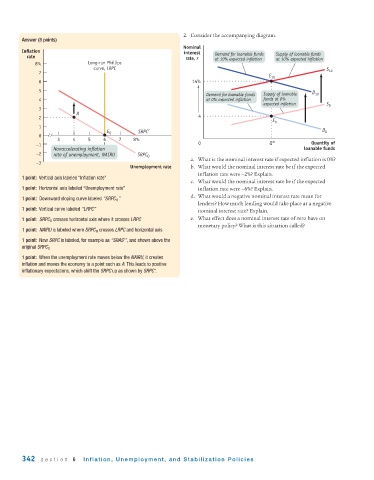
2. Consider the accompanying diagram.
Answer (8 points)
Nominal
Inflation interest
rate rate, r Demand for loanable funds Supply of loanable funds
at 10% expected inflation
at 10% expected inflation
8% Long-run Phillips
curve, LRPC S
7 10
E 10
6 14%
5
Demand for loanable funds Supply of loanable D 10
4 at 0% expected inflation funds at 0%
expected inflation S 0
3
A
2 4
E 0
1
E 0 SRPC’ D 0
0
3 4 5 6 7 8%
–1 0 Q* Quantity of
Nonaccelerating inflation loanable funds
–2 rate of unemployment, NAIRU SRPC 0
–3 a. What is the nominal interest rate if expected inflation is 0%?
Unemployment rate b. What would the nominal interest rate be if the expected
inflation rate were −2%? Explain.
1 point: Vertical axis labeled “Inflation rate”
c. What would the nominal interest rate be if the expected
1 point: Horizontal axis labeled “Unemployment rate” inflation rate were −6%? Explain.
d. What would a negative nominal interest rate mean for
1 point: Downward sloping curve labeled “SRPC 0 ”
lenders? How much lending would take place at a negative
1 point: Vertical curve labeled “LRPC” nominal interest rate? Explain.
1 point: SRPC 0 crosses horizontal axis where it crosses LRPC e. What effect does a nominal interest rate of zero have on
monetary policy? What is this situation called?
1 point: NAIRU is labeled where SRPC 0 crosses LRPC and horizontal axis
1 point: New SRPC is labeled, for example as “SRAS’”, and shown above the
original SRPC 0
1 point: When the unemployment rate moves below the NAIRU, it creates
inflation and moves the economy to a point such as A. This leads to positive
inflationary expectations, which shift the SRPC up as shown by SRPC'.
342 section 6 Inflation, Unemployment, and Stabilization Policies