Page 448 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 448
Problems
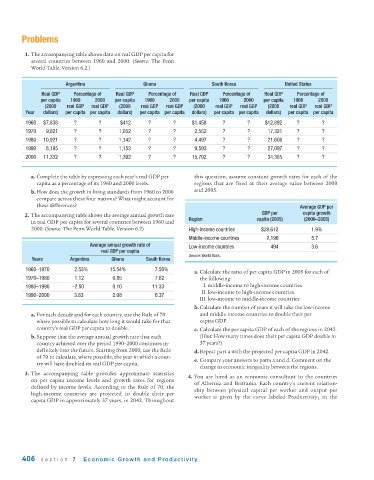
1. The accompanying table shows data on real GDP per capita for
several countries between 1960 and 2000. (Source: The Penn
World Table, Version 6.2.)
Argentina Ghana South Korea United States
Real GDP Per centage of Real GDP Per centage of Real GDP Per centage of Real GDP Per centage of
per capita 1960 2000 per capita 1960 2000 per capita 1960 2000 per capita 1960 2000
(2000 real GDP real GDP (2000 real GDP real GDP (2000 real GDP real GDP (2000 real GDP real GDP
Year dollars) per capita per capita dollars) per capita per capita dollars) per capita per capita dollars) per capita per capita
1960 $7,838 ? ? $412 ? ? $1,458 ? ? $12,892 ? ?
1970 9,821 ? ? 1,052 ? ? 2,552 ? ? 17,321 ? ?
1980 10,921 ? ? 1,142 ? ? 4,497 ? ? 21,606 ? ?
1990 8,195 ? ? 1,153 ? ? 9,593 ? ? 27,097 ? ?
2000 11,332 ? ? 1,392 ? ? 15,702 ? ? 34,365 ? ?
a. Complete the table by expressing each year’s real GDP per this question, assume constant growth rates for each of the
capita as a percentage of its 1960 and 2000 levels. regions that are fixed at their average value between 2000
b.How does the growth in living standards from 1960 to 2000 and 2005.
compare across these four nations? What might account for
these differences? Average GDP per
GDP per capita growth
2. The accompanying table shows the average annual growth rate
Region capita (2005) (2000–2005)
in real GDP per capita for several countries between 1960 and
2000. (Source: The Penn World Table, Version 6.2) High-income countries $28,612 1.9%
Middle-income countries 2,196 5.7
Average annual growth rate of Low-income countries 494 3.6
real GDP per capita
Source: World Bank.
Years Argentina Ghana South Korea
1960 –1970 2.53% 15.54% 7.50% a. Calculate the ratio of per capita GDP in 2005 for each of
1970–1980 1.12 0.85 7.62 the following:
1980–1990 −2.50 0.10 11.33 I. middle-income to high-income countries
II. low-income to high-income countries
1990 –2000 3.83 2.08 6.37
III. low-income to middle-income countries
b.Calculate the number of years it will take the low-income
a. For each decade and for each country, use the Rule of 70 and middle-income countries to double their per
where possible to calculate how long it would take for that capita GDP.
country’s real GDP per capita to double. c. Calculate the per capita GDP of each of the regions in 2042.
b.Suppose that the average annual growth rate that each (Hint: How many times does their per capita GDP double in
country achieved over the period 1990–2000 continues in- 37 years?)
definitely into the future. Starting from 2000, use the Rule d.Repeat part a with the projected per capita GDP in 2042.
of 70 to calculate, where possible, the year in which a coun-
e. Compare your answers to parts a and d. Comment on the
try will have doubled its real GDP per capita.
change in economic inequality between the regions.
3. The accompanying table provides approximate statistics
4. You are hired as an economic consultant to the countries
on per capita income levels and growth rates for regions
of Albernia and Brittania. Each country’s current relation-
defined by income levels. According to the Rule of 70, the
ship between physical capital per worker and output per
high-income countries are projected to double their per
worker is given by the curve labeled Productivity 1 in the
capita GDP in approximately 37 years, in 2042. Throughout
406 section 7 Economic Growth and Productivity