Page 554 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 554
How do we measure utility? For the sake of simplicity, it is useful to suppose that we
A util is a unit of utility.
can measure utility in hypothetical units called—what else?—utils. A utility function
shows the relationship between a consumer’s utility and the combination of goods and
services—the consumption bundle—he or she consumes.
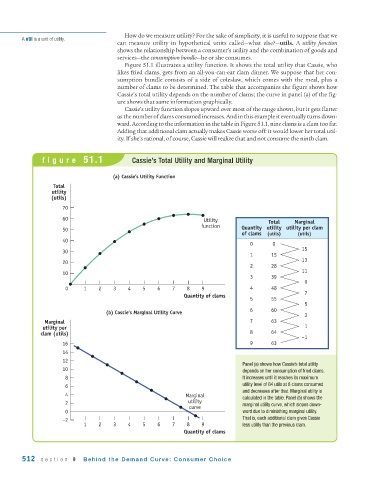
Figure 51.1 illustrates a utility function. It shows the total utility that Cassie, who
likes fried clams, gets from an all-you-can-eat clam dinner. We suppose that her con-
sumption bundle consists of a side of coleslaw, which comes with the meal, plus a
number of clams to be determined. The table that accompanies the figure shows how
Cassie’s total utility depends on the number of clams; the curve in panel (a) of the fig-
ure shows that same information graphically.
Cassie’s utility function slopes upward over most of the range shown, but it gets flatter
as the number of clams consumed increases. And in this example it eventually turns down-
ward. According to the information in the table in Figure 51.1, nine clams is a clam too far.
Adding that additional clam actually makes Cassie worse off: it would lower her total util-
ity. If she’s rational, of course, Cassie will realize that and not consume the ninth clam.
figure 51.1 Cassie’s Total Utility and Marginal Utility
(a) Cassie’s Utility Function
Total
utility
(utils)
70
60 Utility
function Total Marginal
50 Quantity utility utility per clam
of clams (utils) (utils)
40
0 0
30 15
1 15
20 13
2 28
10 11
3 39
9
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 4 48
Quantity of clams 7
5 55
5
6 60
(b) Cassie’s Marginal Utility Curve 3
Marginal 7 63
utility per 1
clam (utils) 8 64
–1
16 9 63
14
12
Panel (a) shows how Cassie’s total utility
10 depends on her consumption of fried clams.
8 It increases until it reaches its maximum
6 utility level of 64 utils at 8 clams consumed
and decreases after that. Marginal utility is
4 Marginal calculated in the table. Panel (b) shows the
2 utility marginal utility curve, which slopes down-
curve
0 ward due to diminishing marginal utility.
–2 That is, each additional clam gives Cassie
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 less utility than the previous clam.
Quantity of clams
512 section 9 Behind the Demand Curve: Consumer Choice