Page 43 - NGTU_paper_withoutVideo
P. 43
Modern Geomatics Technologies and Applications
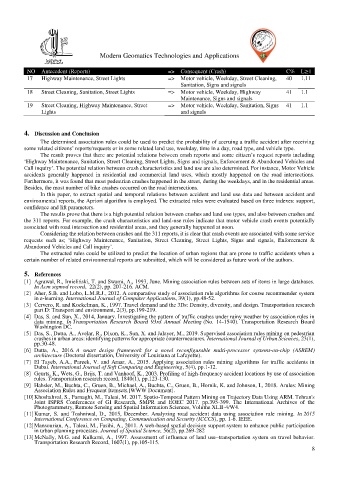
NO Antecedent (Reports) => Consequent (Crash) C% L≥1
17 Highway Maintenance, Street Lights => Motor vehicle, Weekday, Street Cleaning, 40 1.11
Sanitation, Signs and signals
18 Street Cleaning, Sanitation, Street Lights => Motor vehicle, Weekday, Highway 41 1.1
Maintenance, Signs and signals
19 Street Cleaning, Highway Maintenance, Street => Motor vehicle, Weekday, Sanitation, Signs 41 1.1
Lights and signals
4. Discussion and Conclusion
The determined association rules could be used to predict the probability of accruing a traffic accident after receiving
some related citizens’ reports/requests or in some related land use, weekday, time in a day, road type, and vehicle type.
The result proves that there are potential relations between crash reports and some citizen’s request reports including
‘Highway Maintenance, Sanitation, Street Cleaning, Street Lights, Signs and signals, Enforcement & Abandoned Vehicles and
Call inquiry’. The potential relation between crash characteristics and land use are also determined. For instance, Motor Vehicle
accidents generally happened in residential and commercial land uses, which mostly happened on the road intersections.
Furthermore, it was found that most pedestrian crashes happened in the street, during the weekdays, and in the residential areas.
Besides, the most number of bike crashes occurred on the road intersections.
In this paper, to extract spatial and temporal relations between accident and land use data and between accident and
environmental reports, the Apriori algorithm is employed. The extracted rules were evaluated based on three indexes: support,
confidence and lift parameters.
The results prove that there is a high potential relation between crashes and land use types, and also between crashes and
the 311 reports. For example, the crash characteristics and land-use rules indicate that motor vehicle crash events potentially
associated with road intersection and residential areas, and they generally happened at noon.
Considering the relation between crashes and the 311 reports, it is clear that crash events are associated with some service
requests such as; ‘Highway Maintenance, Sanitation, Street Cleaning, Street Lights, Signs and signals, Enforcement &
Abandoned Vehicles and Call inquiry’.
The extracted rules could be utilized to predict the location of urban regions that are prone to traffic accidents when a
certain number of related environmental reports are submitted, which will be considered as future work of the authors.
5. References
[1] Agrawal, R., Imieliński, T. and Swami, A., 1993, June. Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases.
In Acm sigmod record, 22(2), pp. 207-216. ACM.
[2] Aher, S.B. and Lobo, L.M.R.J., 2012. A comparative study of association rule algorithms for course recommender system
in e-learning. International Journal of Computer Applications, 39(1), pp.48-52.
[3] Cervero, R. and Kockelman, K., 1997. Travel demand and the 3Ds: Density, diversity, and design. Transportation research
part D: Transport and environment, 2(3), pp.199-219.
[4] Das, S. and Sun, X., 2014, January. Investigating the pattern of traffic crashes under rainy weather by association rules in
data mining. In Transportation Research Board 93rd Annual Meeting (No. 14-1540). Transportation Research Board
Washington DC.
[5] Das, S., Dutta, A., Avelar, R., Dixon, K., Sun, X. and Jalayer, M., 2019. Supervised association rules mining on pedestrian
crashes in urban areas: identifying patterns for appropriate countermeasures. International Journal of Urban Sciences, 23(1),
pp.30-48.
[6] Dutta, A., 2016. A smart design framework for a novel reconfigurable multi-processor systems-on-chip (ASREM)
architecture (Doctoral dissertation, University of Louisiana at Lafayette).
[7] El Tayeb, A.A., Pareek, V. and Araar, A., 2015. Applying association rules mining algorithms for traffic accidents in
Dubai. International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering, 5(4), pp.1-12.
[8] Geurts, K., Wets, G., Brijs, T. and Vanhoof, K., 2003. Profiling of high-frequency accident locations by use of association
rules. Transportation research record, 1840(1), pp.123-130.
[9] Hahsler, M., Buchta, C., Gruen, B., Michael, A., Buchta, C., Gruen, B., Hornik, K. and Johnson, I., 2018. Arules: Mining
Association Rules and Frequent Itemsets.[WWW Document].
[10] Khoshahval, S., Farnaghi, M., Taleai, M. 2017. Spatio-Temporal Pattern Mining on Trajectory Data Using ARM. Tehran's
Joint ISPRS Conferences of GI Research, SMPR and EOEC 2017. pp.395-399. The International Archives of the
Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Volume XLII-4/W4.
[11] Kumar, S. and Toshniwal, D., 2015, December. Analyzing road accident data using association rule mining. In 2015
International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS), pp. 1-6. IEEE.
[12] Mansourian, A., Taleai, M., Fasihi, A., 2011. A web-based spatial decision support system to enhance public participation
in urban planning processes. Journal of Spatial Science, 56(2), pp.269-282
[13] McNally, M.G. and Kulkarni, A., 1997. Assessment of influence of land use–transportation system on travel behavior.
Transportation Research Record, 1607(1), pp.105-115.
8