Page 48 - NGTU_paper_withoutVideo
P. 48
Modern Geomatics Technologies and Applications
calculated at 10 m of buffer per street. Also, by using the entropy index, land use diversity was calculated in a 10 m buffer per
street.
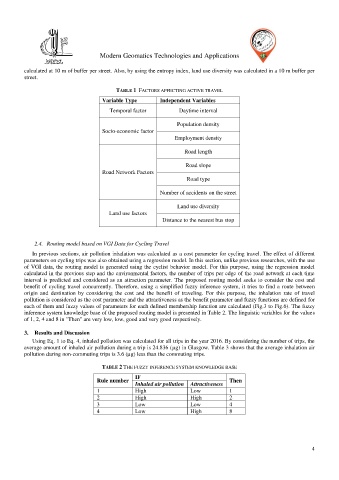
TABLE 1 FACTORS AFFECTING ACTIVE TRAVEL
Variable Type Independent Variables
Temporal factor Daytime interval
Population density
Socio-economic factor
Employment density
Road length
Road slope
Road Network Factors
Road type
Number of accidents on the street
Land use diversity
Land use factors
Distance to the nearest bus stop
2.4. Routing model based on VGI Data for Cycling Travel
In previous sections, air pollution inhalation was calculated as a cost parameter for cycling travel. The effect of different
parameters on cycling trips was also obtained using a regression model. In this section, unlike previous researches, with the use
of VGI data, the routing model is generated using the cyclist behavior model. For this purpose, using the regression model
calculated in the previous step and the environmental factors, the number of trips per edge of the road network at each time
interval is predicted and considered as an attraction parameter. The proposed routing model seeks to consider the cost and
benefit of cycling travel concurrently. Therefore, using a simplified fuzzy inference system, it tries to find a route between
origin and destination by considering the cost and the benefit of traveling. For this purpose, the inhalation rate of travel
pollution is considered as the cost parameter and the attractiveness as the benefit parameter and fuzzy functions are defined for
each of them and fuzzy values of parameters for each defined membership function are calculated (Fig.3 to Fig.6). The fuzzy
inference system knowledge base of the proposed routing model is presented in Table 2. The linguistic variables for the values
of 1, 2, 4 and 8 in "Then" are very low, low, good and very good respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
Using Eq. 1 to Eq. 4, inhaled pollution was calculated for all trips in the year 2016. By considering the number of trips, the
average amount of inhaled air pollution during a trip is 24.836 (µg) in Glasgow. Table 3 shows that the average inhalation air
pollution during non-commuting trips is 3.6 (µg) less than the commuting trips.
TABLE 2 THE FUZZY INFERENCE SYSTEM KNOWLEDGE BASE
IF
Rule number Then
Inhaled air pollution Attractiveness
1 High Low 1
2 High High 2
3 Low Low 4
4 Low High 8
4