Page 8 - Professorial Lecture - Prof Oyedele
P. 8
The radio waves and microwaves at the lower part of the figure have
relatively long wavelengths and are not energetic enough to knock
electrons out of atoms. However, there are other kinds of radiation such as
gamma rays (at the upper part of the figure) having very short wavelength
and which are energetic enough to knock electrons out of atoms or cause
ionization. These are called ionizing radiation. In this lecture we will focus on
ionizing radiation. In fact, when we talk about radiation in nuclear physics
or nuclear science, we are referring to ionizing radiation.
We can also ask from where is ionizing radiation? Ionizing radiation can
come from unstable atoms (and it could be produced in machines). One
can next ask what is meant by unstable atom? To answer this, let us first
briefly discuss what an atom is.
2.2 UNSTABLE ATOMS AND THE RADIATION EMITTED
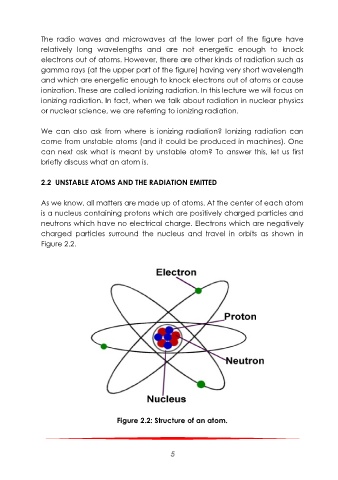
As we know, all matters are made up of atoms. At the center of each atom
is a nucleus containing protons which are positively charged particles and
neutrons which have no electrical charge. Electrons which are negatively
charged particles surround the nucleus and travel in orbits as shown in
Figure 2.2.
Figure 2.2: Structure of an atom.