Page 9 - Professorial Lecture - Prof Oyedele
P. 9
There are different numbers of protons and neutrons in different atoms. An
atom (or element) is defined by the number of protons in its nucleus. For
example, if the number of protons is 8, then the atom is oxygen atom (the
oxygen that we breathe) as shown in Table 2.1.
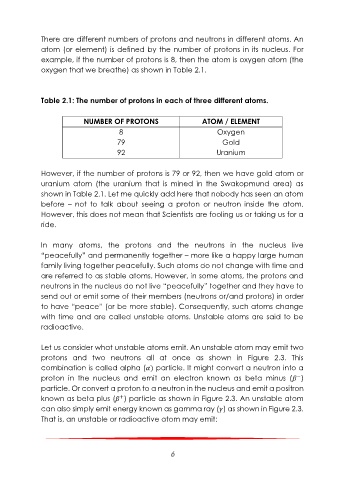
Table 2.1: The number of protons in each of three different atoms.
NUMBER OF PROTONS ATOM / ELEMENT
8 Oxygen
79 Gold
92 Uranium
However, if the number of protons is 79 or 92, then we have gold atom or
uranium atom (the uranium that is mined in the Swakopmund area) as
shown in Table 2.1. Let me quickly add here that nobody has seen an atom
before – not to talk about seeing a proton or neutron inside the atom.
However, this does not mean that Scientists are fooling us or taking us for a
ride.
In many atoms, the protons and the neutrons in the nucleus live
“peacefully” and permanently together – more like a happy large human
family living together peacefully. Such atoms do not change with time and
are referred to as stable atoms. However, in some atoms, the protons and
neutrons in the nucleus do not live “peacefully” together and they have to
send out or emit some of their members (neutrons or/and protons) in order
to have “peace” (or be more stable). Consequently, such atoms change
with time and are called unstable atoms. Unstable atoms are said to be
radioactive.
Let us consider what unstable atoms emit. An unstable atom may emit two
protons and two neutrons all at once as shown in Figure 2.3. This
combination is called alpha ( ) particle. It might convert a neutron into a
proton in the nucleus and emit an electron known as beta minus ( )
−
particle. Or convert a proton to a neutron in the nucleus and emit a positron
known as beta plus ( ) particle as shown in Figure 2.3. An unstable atom
+
can also simply emit energy known as gamma ray ( ) as shown in Figure 2.3.
That is, an unstable or radioactive atom may emit: